2022 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Thomas A. Diller
Dr.Thomas Diller
Degree: PhD
TITLE
Cognitive Preference and Skill Acquisition: The Relationship Between Student Nurse Anesthetists and Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists Thinking Styles
PURPOSE
This study was designed to describe the cognitive preferences of Student Nurse Anesthetists (SRNAs) and CRNAs in the United States.
METHODOLOGY
The researcher used a quantitative, cross-sectional, descriptive correlational design. The researcher administered the Rational Experiential Inventory (REI-40) via electronic survey to enrolled SRNAs and practicing CRNAs. The REI-40 is a validated psychometric tool involving 40 questions. Twenty questions evaluate each decision-making style. Ten questions assess engagement (e.g., enjoyment and reliance), and 10 questions assess the ability (e.g., capability and use) of each style. The demographics (e.g., age, gender, clinical experience, setting, and education) were collected and compared with the cognitive preference.
RESULTS
This study revealed that SRNAs’ and CRNAs’ dominant cognitive preference was rational thinking and experiential thinking was greater than mid-scale. There was no statistical difference in how SRNAs and CRNAs scored on the REI-40 Inventory. Furthermore, there were no strong correlations between years of experience and cognitive preferences. However, there was a statistically significant difference in experiential cognitive ability and engagement when compared by gender identity.
RECOMMENDED CITATION
Diller, Thomas, "Cognitive Preference and Skill Acquisition: The Relationship Between Student Nurse Anesthetists and Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists Thinking Styles" (2022). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. Paper 4088. https://dc.etsu.edu/etd/4088 (Opens in new window)
2021 DNP Student Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Virginia Bradley
Dr. Virginia Bradley
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: PMHNP
TITLE
Promoting AIMS for Tardive Diskinesia: A Program Evaluation
PURPOSE
To ascertain the effects of an updated procedure and screening for tardive dyskinesia (TD) with the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) after initiation of the scale in the electronic medical record (EMR).
METHODOLOGY
Data included patient encounters of patients taking the most frequently prescribed antipsychotics between August 19 and November 26, 2020. All other encounters were excluded. Deidentified data were extracted from the EMR onto an Excel spreadsheet and transferred to SPSS for analysis.
RESULTS
Of 2167 patient encounters (N=2167, n=853), 108 (12.6 %) AIMS forms were completed. The analysis showed that varied provider types completed the AIMS forms, with the NP having the highest adherence rate (46.3 %), MDs had the lowest rate (14.8 %).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Results indicated a need for ongoing education, revised rating scales, and ongoing program evaluations. Improvement suggestions for similar evaluation projects include data analysis showing all prescribed AP-meds and a more complete incorporation of the entire procedure to show prescribing rationale, clinical diagnosis, comorbidities, and screening rationale.
Bradley, V.F., & Weierbach, F. (2021, April). AIMS screening: A procedure evaluation. Poster session presented at East Tennessee State University Conference, Johnson City, TN. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nZg9jOfI0aE
Bradley, V.F., & Weierbach, F. (2021, April). AIMS screening: A procedure evaluation. Poster session presented at East Tennessee State University Conference, Johnson City, TN.
-
Dr. Jennifer Cooke
Dr. Jennifer Cooke
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Implementing A Brief Tobacco Cessation Intervention in Primary Care: A quality Initiative Project.
PURPOSE
The purpose of this quality improvement (QI) initiative was to implement a brief tobacco cessation intervention, such as the 2 A’s and R, into a primary care clinic. The primary outcome was to measure program implementation by nurses. A secondary outcome was measured to see if the implementation of the 2A’s and R screening tool in the primary care clinic improved the number of referrals for smoking cessation treatment.
METHODOLOGY
The design of this project was a QI initiative. As part of the initiative, an educational in-service on using the 2 A’s and R of smoking cessation was presented to the clinical nurses. During the implementation period, clinical nurses recommended the intervention to the known tobacco smokers who accessed the clinic. The nurses then offered a referral to be seen by a primary care provider to discuss smoking cessation or the patient was advised to contact the Tennessee (TN) Tobacco Quitline.
RESULTS
From the 903 patients who accessed the clinic, 44% (n=402) of patients were screened for smoking status. Only 15% (n=61) of patients identified as tobacco users, and from those, 69% (n=42) were not ready to quit, 18% (n=11) were ready to quit and received the Quitline information, and 13% (n=8) stated that they were not ready to quit but requested the Quitline number. None of the patients screened accepted a referral to schedule an appointment to receive smoking cessation.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
This project supports the goal of Healthy People 2030 of delivering a smoking cessation intervention to address health promotion in all persons. Delivering an evidence-based brief tobacco intervention by nurses, provides an exceptional opportunity to increase awareness of tobacco's effects on health. Empowering nurses with health promotion training can boost confidence to provide the intervention that will reach countless patients.
Cooke, J., Short, C., Hemphill, J. (2021, April 7). Implementing A Brief Tobacco Cessation Intervention in Primary Care: A quality Initiative Project. (Poster Presentation). [Virtual conference session]. Epsilon Sigma at- Large Research Day, Johnson City, TN, United States. http://www.etsu.edu/nursing/research/epsig_research_day.php
-
2021 DNP Graduates
Virgina Faye Bradley
Richard G. Brewer, III
Jennifer Marie Cooke
Beth Ann Watts Cruz
Hope Elizabeth Diaz
Elizabeth T. Sparks
Rebecca Lynn Turner
2021 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Jessica L. Bechard
Dr. Jessica Bechard
Degree: PhD
TITLE
Missed Nursing Care: Accounting for Education, Experience, and Job Satisfaction in Registered Nurses
PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to examine missed nursing care in the context of academic preparedness, years of experience, and job satisfaction and determine predictors of missed nursing care.
METHODOLOGY
The MISSCARE survey was distributed electronically to members of the Academy of Medical Surgical Nurses. Descriptive, inferential analysis and regression analyses were conducted using the electronic survey results.
RESULTS
One hundred sixty-eight registered nurses from across the United States were included in the sample for this study. Using the MISSCARE survey, results found there were no significant differences when examining academic preparation, years of experience, or job satisfaction on the amount of care missed at the bedside between ADN, RN-BSN, and traditional BSN nurses. Job satisfaction was the only predictor for missed nursing care, as nurses who are more satisfied are less likely to miss care.
RECOMMENDED CITATION
Bechard, Jessica, "Missed Nursing Care: Accounting for Education, Experience, and Job Satisfaction in Registered Nurses" (2021). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. Paper 3948. https://dc.etsu.edu/etd/3948
-
Dr. Sharon E. Bigger
Dr. Sharon E. Bigger
Degree: PhD
TITLE
Advance Care Planning Protocols and Hospitalization, Rehospitalization, and Emergency Department Use in Home Health
PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to examine the relationship of advance care planning protocols with hospitalization, rehospitalization, and emergency department use rates in U. S. home health agencies (HHA).
METHODOLOGY
Methods. Electronic surveys about ACP protocols were distributed to HHAs. Existing data about demographics, diagnoses, hospitalization, rehospitalization, and ED use were accessed online via CMS websites. Descriptive and regression analyses were conducted using the electronic survey results and the existing data.
RESULTS
Associations between the variables were observed and compared to the hypotheses. Statistical significance was found in the relationship between ACP protocols and hospitalization, where one increased the other increased. Several trends were found: Agencies with increased total percentage of cardiac and pulmonary diagnoses tended to have increased hospitalization rates; agencies with increased average age of patients tended to have increased ACPP scores; and agencies with increased proportion of Black patients tended to have higher hospitalization rates.
RECOMMENDED CITATION
Bigger, Sharon, "Advance Care Planning Protocols and Hospitalization, Rehospitalization, and Emergency Department Use in Home Health" (2021). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. Paper 3858. https://dc.etsu.edu/etd/3858
-
Dr. Jessica E. Patrylo
Dr. Jessica E. Patrylo
Degree: PhD
TITLE
Examining Predictors of Attitudes and Knowledge of Registered Nurses and Nursing Students in Tennessee toward Pregnant and Perinatal Women with a Substance Use Disorder
PURPOSE
The purpose of this descriptive cross-sectional non-experimental study was to examine how formal SUD nursing education, personal experiences, and participant characteristics predict attitudes and knowledge of nursing students and practicing perinatal nurses in Tennessee toward pregnant and perinatal women with an SUD.
METHODOLOGY
The sample consisted of 262 nursing students and 99 perinatal nurses across the west, middle, and eastern regions of Tennessee. A linear multiple regression showed that having a personal experience with a close friend with an SUD was predictive of improved knowledge scores of pregnant and perinatal SUDs
RESULTS
Independent samples t-tests were non-significant between formal SUD nursing education and attitudes and knowledge. Additionally, non-significant findings were seen between having a personal experience with a family member with an SUD and attitudes and knowledge. The findings suggest that Tennessee nursing education efforts were not influential in positively affecting attitudes and knowledge scores toward pregnant and perinatal women with an SUD. Future studies focused on exploring various educational interventions to promote knowledge, improve attitudes, and empathy in nursing populations toward pregnant and perinatal women with an SUD are warranted.
RECOMMENDED CITATION
Patrylo, Jessica, "Examining Predictors of Attitudes and Knowledge of Registered Nurses and Nursing Students in Tennessee toward Pregnant and Perinatal Women with a Substance Use Disorder" (2021). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. Paper 3951. https://dc.etsu.edu/etd/3951
-
Dr. Dynisha M. Wigginson
Dr. Dynisha M. Wigginson
Degree: PhD
TITLE
“I Done Been Through Hell”: An Existential Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Fathers Who Have Lost a Child
PURPOSE
Fathers’ experiences at their child’s end of life, as an individual phenomenon, is overlooked and ignored. Hence, significant knowledge gaps exist related to the repeated exclusion of fathers’ individual experiences. This study aimed to begin to fill this gap.
METHODOLOGY
Using the lens of Merleau-Ponty, this existential phenomenological study aimed to describe the lived experiences of fathers who have experienced their child’s end of life. Using an unstructured interview process, a total of eight fathers participated in one-on-one interviews via Zoom or telephone. Data analysis and interpretation was conducted using an iterative analytic process, whereby transcripts were read and examined line-by-line to identify figural themes against the ground.
RESULTS
Merleau-Ponty’s existential grounds of time, body, others, intentionality, and perception are interwoven throughout fathers’ individual stories. The following four themes emerged: (a) “I done been through hell”, (b) “I felt helpless”, (c) “I’m a protector”, and (d) “Who is there to help me?”. Additionally, five subthemes describing fathers’ emotional pain, forgetfulness, and masculine inabilities emerged. Greater understanding of fathers’ lived experiences requires serious attention and more research is needed. There are implications that have the potential to impact nursing care and the creation of meaningful nursing interventions for fathers at their child’s end of life
RECOMMENDED CITATION
Wigginson, Dynisha, "“I Done Been Through Hell”: An Existential Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Fathers Who Have Lost a Child" (2021). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. Paper 3888. https://dc.etsu.edu/etd/3888
2020 DNP Student Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Rebecca T. Clark
Dr. Rebecca T. Clark
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: FNP
TITLE
Monitoring Prediabetes Screening in Two Primary Care Offices in Rural Appalachia: A Quality Improvement Project
PURPOSE
Prediabetes is major risk factor for the development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). One-third of the population in the United States has prediabetes, but 90% remain undiagnosed because healthcare providers are not performing screenings. The purpose of this process improvement project was to implement prediabetes screening, prediabetes identification, and a referral process to a registered dietician/certified diabetes educator (RD/CDE) in two Federally Qualified Health Centers.
METHODOLOGY
This was a quality improvement project conducted over a six-week period after receiving approval from the University’s Internal Review Board. The risk assessment tool was the “Are you at risk for Type 2 Diabetes?” Evidence-based treatment interventions included referral to a RD/CDE, education on 5%-7% total body weight loss, and/or 150 minutes of exercise per week. The screening results and interventions data were coded, extracted into SPSS Version 25, and analyzed. Aggregate data reported patient characteristics, quantity of screenings performed, evidence-based recommendations offered, and patient risk factors for prediabetes.
RESULTS
The percentage of patients at risk for prediabetes was 41.3% (n=111). The most frequent risks were identified as overweight, history of hypertension, family history of T2DM, and older age. Providers offered education on weight loss 68.5% (n=76) and exercise 76.6% (n=85) but referred 33.3% (n=37) patients for nutrition education. The screening rates were 52.3% (n=176) and 72.5% (n=244) in clinics A and B respectively. A gap remains in using evidence-based recommendations to decrease risk of prediabetes. Prediabetes screening identified a greater percentage of persons in this population.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Consistent implementation of prediabetes risk assessment and following evidence-based interventions would positively impact patient outcomes. Providing appropriate education and resources will aid healthcare providers in preventing chronic disease. This project can be easily implemented to identify persons at risk for prediabetes.
Clark, T., Mullins, C.M., & Hemphill, J. (2020, April 21-22). Monitoring Prediabetes Screening in Two Primary Care Offices in Rural Appalachia: A Quality Improvement Project. (Poster Presentation). Appalachian Student Research Forum, Johnson City, TN, United States. https://www.etsu.edu/studentresearch/ (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
-
Dr. Georgiana C. Hogan
Dr. Georgiana C. Hogan
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Constipation in the Long-Term Care Resident
PURPOSE
An evidence-based clinical practice guideline was developed to prevent and manage constipation in the long-term care (LTC) resident.
METHODOLOGY
A literature review was completed, and evidence was evaluated and included into the initial draft recommendations. The guideline was reviewed for content validity using a Delphi Committee of clinical experts in gastroenterology, geriatrics, and pharmacy. The updated guideline was presented to an interdisciplinary team of long-term care residents. Participants were asked to review and complete a survey regarding clinical applicability of the guideline. Finally, the guideline was evaluated by a group of Doctoral prepared practicing nurse practitioners using the AGREE II instrument.
RESULTS
Thirty-one interdisciplinary members participated in the education session and 30 surveys were received. Overall, the interdisciplinary team members agreed or strongly agreed the guideline was clinically applicable. The AGREE II appraisers aggregated scores were 85% or higher in every domain, indicating the guideline is high in quality.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The information from the guideline highlights several clinical pearls. The goal should be regular bowel movements, avoid periodic cleanouts. Do not use milk of magnesia or magnesium citrate with the LTC resident. They are contraindicated in those with renal impairment, congestive heart failure, electrolyte imbalance, risk for dehydration, and hypertension. Do not use enemas or soap suds buckets. These medications may result in perforation, electrolyte imbalances, renal failure, sepsis, and death (<4%). Use the digital rectal exam to assess constipation, especially to assess for fecal impaction. Fecal impaction can lead to severe morbidity and mortality, consider admission to the Emergency Department. Add more prunes and fiber. Hospitalization can lead to constipation. Do not discontinue scheduled bowel medications. Prescribe the max dosage of bowel medication before attempting another medication.
Hogan, G.C. (2020, April). Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Constipation in the Long-Term Care Resident. (Poster Presentation). The Charles George VA Medical Center Community Living Center, Asheville, NC, United States.
Hogan, G.C. (2020, April). Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Constipation in the Long-Term Care Resident. (Podium Presentation presented to the Charles George VA Medical Center Interdisciplinary Team, Asheville, NC, United States.
-
Dr. Rhonda Morris
Dr. Rhonda Morris
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Advance Care Planning in Primary Care: Evaluation of the Conversation Starter Toolkit Implementation
PURPOSE
Advance care planning is a standard of care designed to help patients understand illness progression, anticipate outcomes, and to plan for the last stages of life. Despite three decades of demonstrated benefits in the United States, advance care planning still has not become routine practice and only one-third of adults have advance directives. Primary care clinicians provide care throughout long-standing relationships with forty-five million Americans who are living with chronic illness. The purpose of this project was to enhance the number of patient-provider advance care planning discussions, leading to patients making informed decisions about advance directives.
METHODOLOGY
This was a quality improvement project where providers initiated the Conversation Starter Kit for patients presenting for Medicare Annual Wellness Visits in a rural primary care setting in the Southeastern United States. Aggregate data was collected from the electronic health record by the clinic staff to include the number of patients with existing advance directives, the number of advance care planning conversations documented, and the number of Conversation Starter Kits documented pre- and post-implementation. Inclusion criteria were Medicare or dual-eligible patients aged 50 years or older presenting for a Medicare Annual Wellness Visit. Exclusion criteria were patients less than 50 years old or those presenting for a visit other than a Medicare Annual Wellness Visit.
RESULTS
The providers’ advance care planning discussion documentation increased by 6.7% and the providers’ advance directive documentation increased by 9.5%. Integrating the Conversation Starter Kit into Medicare Annual Wellness Visits in a primary care practice increased and opened up provider-patient conversations for end-of-life care planning.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Improving advance care planning discussion leads to patients making informed decisions about end-of-life care.
Morris, R., Mullins, C.M., & Sargsyan, A. (2020, April 21-22). (Poster Presentation). Appalachian Student Research Forum, Johnson City, TN, United States. https://www.etsu.edu/studentresearch/ (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
-
Dr. Nancy Sciara
Dr. Nancy Sciara
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Adherence to Perinatal Depression Screening Guidelines: A Retrospective Review
PURPOSE
The purpose of the project was to evaluate adherence to depression screening guidelines with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), in a rural obstetrics and gynecology practice in North Carolina. The project aims were to: (a) conduct a twelve month retrospective chart review to quantify the number of completed screens, (b) determine the number of positive screens, (c) determine if referrals were made for positive screens, and (d) disseminate recommendations based on project outcomes.
METHODOLOGY
Through electronic medical records review, appointments were evaluated to determine when patient visits occurred, then the charts were reviewed on the specific date to determine if the PHQ-9 was completed. If the screening was completed, the screening score was obtained, and provider notes were reviewed to determine if the patient was referred for further treatment.
RESULTS
The data (N= 1859) were analyzed in Excel by month, visit type, score result, and presence of referral when indicated. During new OB visits, depression screens were completed 23% of the time and for the postpartum visits, the completion rate was 67%. Cumulatively, depression screens were completed at 44% of the perinatal visits. Referrals were offered at 12% rate with positive depression screening results. Findings of the project indicated that screening and referral were inconsistent. There were times when screens were completed, with positive results for depression however documentation did not indicate that there was discussion between patient and provider. Additionally, there was lack of documentation when the patient indicated on the screen that she “would be better off dead”.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The findings of this project indicated a need for policy creation to streamline consistent screenings. Educating the clinical staff and providers regarding the PHQ-9, communication of screening scores, and importance of referral to a mental health provider will improve patient outcomes.
Sciara, N. (2020, April 20-21). Adherence to perinatal depression screening guidelines: A retrospective review [Conference session]. Appalachian Student Research Forum (ASRF), Johnson City, TN, United States. research@etsu.edu (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
Sciara, N. (2020, April 3). Adherence to perinatal depression screening guidelines: A retrospective review [Conference session]. Epsilon Sigma at-Large Research Day, Morristown, TN, United States. stephanie.conder@lmunet.edu (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
-
Dr. Drew S. Turner
Dr. Drew S. Turner
Degree: DNP
Degree Concentration: Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Evaluation of a Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper and Referral Protocol
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project is to evaluate the effectiveness of a mental health toolkit: the Tennessee Suicide Prevention Network (TSPN) Suicide Behavior Procedure Checklist. To address teachers’ and staff members’ knowledge of suicide prevention, an evidence-based suicide prevention gatekeeper training program called Question, Persuade, Refer (QPR) was implemented.
METHODOLOGY
This Quality Improvement Project is designed as an effort to help generate a sustainable change in suicide monitoring practices at a private, Christian school located in the Northeastern part of the United States. Step 1: Provide suicide prevention gatekeeper training by Question, Persuade, Refer (QPR) Gatekeeper Training. Used a pre-test, post-test, and six weeks post retention test to monitor teachers and staff members knowledge level on suicide prevention. Step 2: Education provided on the TSPN Suicide Behavioral and Procedural Checklist and Mental Health Toolkit. Step 3: Monitor the number of students at risk of suicide and use of the toolkit.
RESULTS
The increase in knowledge was significant when comparing the pre-test to the initial post-test (p<0.001) and the six-week post-retention test (p<0.001). Three students were identified at risk of suicide during an 8-month monitoring period. Resources from a mental health tool kit were tracked also.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Based on the findings, it is recommended that similar programs be implemented in schools to reduce the rate of adolescent suicide.
Turner,D. (2020, April 21-22). Evaluation of a Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper and Referral Protocol (Poster Presentation). Appalachian Student Research Forum, Johnson City, TN, United States. https://www.etsu.edu/studentresearch/ (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
Turner,D. (2020, March 26). Evaluation of a Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper and Referral Protocol (Podium Presentation). Tennessee Suicide Prevention Network Northeast Regional Meeting, Johnson City, TN, United States https://www.tspn.org (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic).
-
2020 DNP Graduates
2020 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Melinda A. Bogardus
Dr. Melinda A. Bogardus
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
The Experiences and Well-being of Mexican Immigrant Women Living in Traditionally non-Latinx Communities in Western North CarolinaPURPOSE
North Carolina has, in recent decades, experienced significant growth in its Latinx, and more particularly Mexican immigrant population. As a traditionally non-Latinx state, or a state without a long-standing, large Latinx population, many communities and healthcare and service providers within North Carolina still lack knowledge, resources, and skills needed to serve and support Latinx immigrant populations well.METHODOLOGY
Guided by interpretive description, this qualitative study on Mexican immigrant women in Western North Carolina sought to gain knowledge and understanding of what it is like for this subgroup of immigrants to live in a traditionally non-Latinx region and how immigration has affected their well-being. Asking women to discuss their experiences in the context of immigration as a way of learning about their well-being was inspired by scholars who have asserted immigration to be an important determinant of health and significant life experience.RESULTS
Individual interviews with 12 Mexican immigrant women generated five themes: 1) Differences and disruption, 2) Losing to Gain, 3) Living with Risks and Limitations, 4) From Lost to Found, and 5) Resilience and Adaptation. Together these themes highlight sacrifices and struggles, strengths and resources, and gains and hope that have affected these women’s well-being and paint an overall picture of resilience and adaptation in spite of losses, difficulties, risks, and limitations incurred by immigrating. These findings argue for use of a strengths-based approach when interacting with Mexican immigrant women to improve healthcare and other services and promote their well-being and integration in their NC communities. -
Dr. Amy Holder
Dr. Amy Holder
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
The relationship of self-efficacy and clinical reasoning of undergraduate nursing students
PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to determine if a relationship exists between a student’s self-efficacy of clinical reasoning ability and a student’s actual clinical reasoning ability. In addition, this study seeks to determine the relationship between a student’s self-efficacy of clinical reasoning and a student’s locus of control. Finally, this study sought to determine if perceived self-efficacy of clinical reasoning changed over time.
The ability to successfully navigate the process of clinical reasoning is critical to providing safe, effective care for patients. For nurses, this process is developed in nursing school. Unfortunately, there is evidence to suggest that newly graduated nurses struggle to navigate this process successfully, placing patients’ safety in jeopardy. While much research has been devoted to the development of clinical reasoning in students, little is known about factors that affect the development of clinical reasoning in the student population.
METHODOLOGY
A partial correlation was conducted to determine the relationship between students’ perceived self-efficacy of clinical reasoning and the students’ actual clinical reasoning ability. In addition, a one-way ANOVA to determine changes over time and reliability assessment of the Nurses’ Clinical Reasoning Scale were performed.
RESULTS
A sample of 52 undergraduate nursing students from across the United States were included in this study. There was no significant relationship between the students’ perceived self-efficacy of clinical reasoning and the students’ actual clinical reasoning ability, nor was there a significant change in perceived self-efficacy scores over time.
By understanding the impact certain factors have on the development of clinical reasoning ability in students, educators are better equipped to identify those that might struggle to develop clinical reasoning and intervene early in the process of development. More research is needed to fully understand the role these factors play in the development of clinical reasoning.
-
Dr. Andrea S. Poynter
Andrea S. Poynter
Ph.D., MSN, RN
TITLE OF PROJECT
The Lived Experience of Obesity, Spirituality, and Health Behaviors in African American Women
PURPOSE
Obesity is one of the fastest-growing health concerns impacting all racial, ethnic, gender, and socioeconomic groups in the United States of America. More than one-third of the U.S. adult population is classified as being obese (Obesity Society, 2014). Novak and Brownell (2012) identified that “obesity rates are consistently rising higher each year than in previous years” (p. 2345). Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in all races and genders within the US with African American women comprising a majority of those impacted by this chronic health condition. Obesity rates are well documented within the literature but what is lacking is the role spirituality may play in obese African American women and their health behaviors. The purpose of this qualitative, phenomenological study was to explore and describe the lived experiences of obese African American women with attention and focus on weight, health behaviors, and spirituality.
METHODOLOGY
This study consisted of participant recruitment from various social organizations, beauty salons, and faith-based organizations. A naturalistic setting with a descriptive approach was taken to interview the participants and all recorded interviews were transcribed and utilized for data analysis. The analysis method for this study was the qualitative content analysis process.
RESULTS
Upon completion of data analysis, the identification of three themes, who I am, the weight I bear, and power struggles, assisted with recognizing the gaps and concerns that supported the researcher in painting a picture of the lived experiences of obese African American women. Recommendations included diversifying healthcare providers, implementing community-based interventions and research, and completing knowledge assessments before education. A future research opportunity includes utilizing beauticians as lay community members of a research study to provide education and initiate hard conversations regarding weight, health behaviors, and interventions to their clientele.
-
Dr. Cathy Simpson
Cathy Simpson
PhD, RN
TITLE OF PROJECT
Undergraduate Nursing Students’ Learning Style Preferences and Preferred Faculty Teaching Methods Compared to the Actual Methods Used by Faculty
PURPOSE
The aim of this study was to examine the generational differences of undergraduate nursing students’ learning style preferences and their preferred faculty teaching methods to the teaching methods used most often by nursing faculty in the classroom. Nursing educators are responsible for creating learning environments that are effective for students that are in different generations and nursing educational pathways. Each generational cohort brings a collective set of characteristics, expectations, and preferences to the classroom, challenging educators to balance the generational learning styles of all students with respectable, evidence-based, pedagogical approaches. This study was one of the first to explore Generation Z’s preferred teaching method preferences used in the classroom.
METHODOLOGY
Both descriptive and inferential statistical procedures were used for this study. A one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test was performed to evaluate the difference between each of the learning style preferences, followed by a Kruskal-Wallis test that compared the generational differences to the learning styles. A Likelihood-ratio Chi-square (LR χ2) was performed to assess for association between generational cohorts and their preferred teaching methods used in the classroom.
RESULTS
One hundred eighty-four undergraduate nursing students; and sixty-seven nursing faculty from ten Southeastern states were included in the sample for this study. Using the Index of Learning Styles® survey, results found nursing students had either a balanced active/reflective and sequential/global learning style, or a sensing or visual learning styles. With regards to preferred teaching methods, lecture, and the use of visual aids in the classroom were identified as the top teaching methods preferred by both student and faculty participants. Nurse educators are responsible for creating learning environments that are inclusive of students from diverse generational cohorts, spanning six decades and in multiple nursing educational pathways. These results provide new information for nursing educators to utilize in various academic settings.
2019 DNP Student Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Karen L. Burchfield
Dr. Karen L. Burchfield
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Executive Leadership
TITLE
Evaluation of Lean Standard Work Methodology to improve Medication Administration Record Completion in an Urban Elementary School System
PURPOSE
Enhance completion of medication administration records (MAR) in school systems.
METHODOLOGY
Post-intervention data was collected from the four schools and provided to evaluate as either complete or incomplete as a whole. One school did not have incomplete MARs before or after implementation of the intervention. Therefore, statistical analysis was conducted on data from only three schools, using the Chi-square test. Two of the three schools demonstrated a significant decrease in incomplete MARs after the intervention and the overall improvement was 34.1%.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Follow nursing professional bodies position statements and recommendations for establishing policies and procedures for medication administration to include MAR completion.
-
Dr. Tonia W. Hale

Dr. Tonia W. Hale
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Executive Leadership
TITLE
Impact of a Standardized Discharge Intervention on Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) Scores
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to measure the impact of a standardized discharge packet on two orthopedic units in an acute hospital in the following HCAHPS domains: communication with nurses, communication about medications, discharge information, and care transition.
METHODOLOGY
A quality improvement project in an acute hospital setting in east Tennessee was conducted on English-speaking patients between 18 and 75 years of age. The intervention was a standardized discharge packet using the teach-back method.
RESULTS
Descriptive statistics was used for the data analysis using independent t-test and SPSS 24.0. The results were grossly different on Unit A and Unit B. “Tell you what new medicine was for” was statistically significant on both units with a P < .001. The variation in results may have been due to 75 nurses floating into these units during the implementation period. Unit A received 80% of the nurse floaters and there were only improvements in 1 of 10 questions; however, Unit B experienced improvements in 7 out of 10 questions under the four HCAHPS domains. Unit B had one nurse primarily completing the discharge intervention. Therefore, the results suggest that the standardized discharge packet positively impacted the scores on Unit B.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The utilization of a standardized discharge packet may improve Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems scores and ultimately, improve financial incentive payments in the acute hospital setting.
Poster Presentation
-
Dr. Joseph Harris
Dr. Joseph Harris
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Improvements in Addressing Patient Smoking Status on an Assertive Community Treatment Team by Implementing the Five A’s of Smoking Cessation
PURPOSE
The risks of tobacco use are especially problematic in patients with severe and persistent mental illness (SPMI), yet any Assertive Community Treatment Team (ACTT) staff members were not addressing patient smoking status. The purpose of this quality improvement project was to assess the ACTT’s adoption of a new program grounded in the 5 A’s of smoking cessation and to enhance ACTT staff knowledge regarding smoking cessation and tobacco cessation myths.
METHODOLOGY
The rate in which ACTT staff addressed smoking with patients was compared for the four weeks prior to an educational intervention and for 12 weeks post-intervention. ACTT staff also completed an anonymous pre- and post-intervention survey to measure any changes in perceptions and knowledge about smoking cessation. Descriptive statistics were utilized to analyze the data.
RESULTS
The percentage of visits in which staff addressed smoking increased from 4.6% to 12.0% post-intervention and patients were referred to the quitline. There was also a reduction in the acceptance of tobacco cessation myths and increased knowledge and confidence that patients with SPMI can quit smoking.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The smoking cessation program improved staff knowledge related to smoking cessation, equipped staff with resources to help patients to quit smoking, reduced the acceptance of tobacco cessation myths, and facilitated most staff members (70%) to assist patients to quit smoking during the project. Patients with mental illness are interested in quitting smoking and are more apt to do so when health professionals are encouraging them to quit smoking. Nurses who adopt a strong position on smoking cessation can act as champions of change when executing smoking cessation programs.
-
Dr. Pamela Ann Trent
Dr. Pamela Ann Trent
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
The Effects of Nurse-Initiated Protocols on Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Outcome Measures in the Emergency Department
PURPOSE
Annual emergency department (ED) visits continue to rise, increasing the risk for prolonged wait times and negative consequences. This necessitates innovative approaches to improve efficiency and outcomes. The use of nurse-initiated protocols upon patient arrival to the ED expedites care through prompt ordering and completion of diagnostic tests. In turn, throughput and departmental performance measures linked to efficiency and reimbursement may be improved. The purpose of this project was to evaluate the effects of nurse-initiated triage order sets on Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services outcome measures for discharged patients.
METHODOLOGY
De-identified, aggregated data specific to reportable outpatient outcome measures in the ED was collected over a three-month period (N=92) in 2018 and compared to data of the same time frame in 2017. The efficiency-related outcome measures included median time from ED arrival to ED departure for discharged ED patients (LOS), door to diagnostic evaluation by a qualified medical professional, left without being seen (LWBS) rate, and nurse use of standing order sets.
RESULTS
The number of nurse-initiated protocols increased significantly during the study period (Z = -2.31, P = 0.02). A statistically significant decrease was found in the LOS of discharged patients (Z = -2.33, P = 0.02) and door to provider evaluation time (Z = -9.66. P < 0.01). There was a non-significant decrease in the LWBS rate (Z = -0.72, P = 0.48).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
A relationship exists between the use of protocols and clinically and statistically significant improvements in ED performance measures. It is likely that protocols may benefit emergency departments by reducing ED overcrowding, improving throughput, and increasing reimbursement through CMS-related value-based purchasing models. In turn, patient outcomes may be improved by mitigating the negative effects of prolonged ED wait times.
-
2019 DNP Graduates
Afolake Awolaja
Rony Boe
James Coombs
Joanna Dymora
Bupe Habiyambere
Joseph Harris
Ashley Lockhart
Kendra O’quinn
Pamela Trent
Mathew WoodJulia Blocker
Karen Burchfield
Hanna Crawford
Rebecca Garrett
Tonia Hale
Ryan Kerrins
Jill Newton
Latisha Toney
Lisa Waye
2019 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Evelyn P. Brewer
Dr. Evelyn P. Brewer
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
Contemporary Nursing in Rural Appalachia: A Hermeneutic StudyABSTRACT
Nurses make up a significant source of direct care for individuals, families, and communities. The problematic distribution of nurses and the potential to lose practicing nurses emphasizes the importance of retention and support of nursing professionals, especially in rural locations. One of the best ways to discover what is important to nurses is to ask and listen to the replies. The focus for this dissertation is the lived experience of registered nurses in a six-county area in three adjoining states in rural South Central Appalachia. The purpose of this study is to interpret and understand the lived experience of contemporary RN practice in rural Appalachia. The two aims of the study are to 1) understand the lived experience of contemporary nurses in rural Appalachia, and 2) understand the lived experience of nurses as they relate to the place of residence and the place of employment. The chapters include the research proposal and three manuscripts. Chapter 1 contains the background and significance. Chapter 2 is the literature review. Chapter 3 includes sampling and recruitment in rural areas. The findings are discussed in Chapter 4. Chapter 5 contains an integration of all manuscripts, discussion of the contribution to nursing science, direction for future research, and implications for nursing practice. Manuscripts are ready for submission and will be formatted per author guidelines prior to submitting. The first manuscript, “Perceptions of Nursing in Appalachia: A State of the Science Paper,” is a literature review. The manuscript reviews the literature surrounding nurses in Appalachia. It was published in the Journal of Transcultural Nursing in January, 2018 (Brewer, 2018). The second manuscript, “The Lived Experience of Nursing in Appalachia: Sampling and Recruitment,” examines the researcher’s experience with sampling and recruitment. The second manuscript will be submitted to the Online Journal of Rural Nursing and Health Care. The third manuscript, “Living and Working as a Nurse in Appalachia: A Phenomenological Study,” provides findings, implications, and future research. This paper describes findings and identifies themes of the data. The third manuscript is ready for publication to the Journal of Transcultural Nursing. The conclusion presents dissertation summary comments.
2018 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Deborah Henry
Dr. Deborah Henry
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
Rediscovering the Art of Nursing for Nursing PracticePURPOSE
The art of nursing is discussed throughout nursing literature but research on the topic is lacking. The purpose of this research was to reveal experiences of the art of nursing. Nurses were asked to describe experiences about the art of nursing from their own nursing practice.METHODOLOGY
This study was qualitative in nature and used a phenomenological approach to answer the research question, “What is the experience of the art of nursing in nursing practice?” The study was guided by the philosophical stance of Merleau-Ponty and the research strategies of Thomas and Pollio.RESULTS
Participants included nurses who had experience using the art of nursing to provide patient care and were willing to articulate these experiences. With IRB approval, eleven nurses participated in the interview process. Results demonstrate the art of nursing in nursing practice includes showing up, staying, and helping patients, connecting to patients, intuitive caring, and making a difference in the lives of both patients and nurses. Findings from this study confirm the art of nursing as an essence of nursing with implications for nursing practice, nursing education, and future research. -
Dr. Kristi Miller
Dr. Kristi Miller
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
Effect of Root Cause Analysis on Pre-Licensure, Senior-Level Nursing Students’ Safe Medication Administration PracticesPURPOSE
The aim of this study was to examine if student nurse participation in root cause analysis has the potential to reduce harm to patients from medication errors by increasing student nurse sensitivity to signal and responder bias.
Schools of nursing have traditionally relied on strategies that focus on individual characteristics and responsibility to prevent harm to patients. The modern patient safety movement encourages utilization of systems theory strategies like Root Cause Analysis (RCA). The Patient Risk Detection Theory (Despins, Scott-Cawiezell, & Rouder, 2010) supports the use of nurse training to reduce harm to patients.
METHODOLOGY
Descriptive and inferential analyses of the demographic and major study variables were conducted. Validity and reliability assessments for the instruments were performed.
The Safe Administration of Medications-Revised Scale (Bravo, 2014) was used to measure sensitivity to signal. The Safety Attitudes Questionnaire (SAQ; Sexton et al., 2006) was used to assess responder bias; this was the first use of this instrument with nursing students.
RESULTS
The sample consisted of 125 senior-level nursing students from three universities in the southeastern United States. The SAQ was found to be a valid and reliable test of safety attitudes in nursing students. Further support for the validity and reliability of the SAM-R was provided. A significant difference in safety climate between schools was observed. There were no differences detected between the variables.
The results of this study provide support for the use of the SAQ and the SAM-R to further test the PRDT, and to explore methods to improve nursing student ability to administer medications safely.
2017 DNP Student Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Erin Elizabeth Bailey
Dr. Erin Bailey
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
BSN-DNP Perceptions of the DNP Essentials and How They Apply to Future Advance Practice Roles
PURPOSE
Researchers throughout available literature have shown growth in DNP programs, positive perceptions of the DNP degree, and DNP graduates struggling to actualize DNP education to practice. However, BSN-DNP students’ perceptions of the foundation of the degree have not been assessed. The purpose of this study is to explore BSN-DNP students’ perceptions of the DNP Essentials, upon which the program is based, and how they see the Essentials apply to their future advanced nursing practice roles. The study is informed by Benner’s (1982) theory of Stages of Clinical Competence.
METHODOLOGY
A qualitative descriptive study design was used and sample participants were full-time students at a state university’s BSN-DNP program in the southern region.
RESULTS
The findings from the data analysis show three themes emerging around the general concept of Becoming a DNP, which included Uncertainty of Role, Preparation for Role, and Values of Role.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Implications of the findings provided insight into the perceptions of BSN-DNP students on the DNP Essentials and how they will be applied to future practice. The findings inform DNP faculty regarding students’ understanding of the Essentials and how to better connect the Essentials to practice.
-
Dr. Mandy Marie Brannen
Dr. Mandy Marie Brannen
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Improving Health Outcomes for Mother and Baby through PCP Education
PURPOSE
Postpartum depression is a serious mental illness that can have negative consequences to the mother and baby. Depression screening takes place at prenatal and postpartum visits; however, subsequent follow-up rates for mental health care is lacking. This project assessed primary care providers’ perceptions, knowledge, interventions, and barriers associated with postpartum depression.
METHODOLOGY
A pre-experimental pre-test post-test design was used to assess primary care providers working with pregnant women, and up to 12 months postpartum. Providers were employed at a federally qualified health center and were assessed on the topic of depression. A four-point Likert scale was utilized with the highest value indicative of the most positive response. An evidence-based educational intervention, given by a clinical expert on perinatal mood disorders was followed by the post-test questionnaire. Data was analyzed with the Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test.
RESULTS
Findings suggest that providers have a more positive response about knowledge, interventions, and barriers associated with postpartum depression following an educational intervention. Additionally, mental health care follow-up rates increased from 10% to 12.5% following the educational intervention.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Quality improvement efforts involving evidence-based educational interventions on postpartum depression, given to primary care providers, may assist in improving health outcomes for both mother and baby.
-
Dr. Holly Dillon Dockery
Dr. Holly Dillon Dockery
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
AGNP
TITLE
The Development, Implementation, and Evaluation of a Web-Based Learning Module on Advanced Care Planning: Enhancing the Knowledge of Clinical and Advance Practice Nurses in Tennessee
PURPOSE
The use of a web-based learning modules has been suggested as a way to reach out to healthcare professionals to improve the processes surrounding Advanced Care Planning (ACP) for adults with chronic conditions. The purpose of this project is to develop, implement, and evaluate an ACP educational program for clinical nurses and advance practice nurses in Tennessee.
METHODOLOGY
The program is guided by the PRECEDE-PROCEED model, which has been shown to be effective for healthcare education. The non-experimental design included a needs assessment, personal profile/demographic survey, an educational intervention in the form of a web-based learning module with associated pre-post-tests, and program evaluation.
RESULTS
71 responses were received from an electronic needs assessment survey and 21 participants were recruited for program completion. Knowledge was increased after completion of the program and additional information was received from participants’ feedback substantiating the need for education on advance care planning and related topics.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The use of a web-based learning module is likely to be effective to enhance the knowledge of nurses practicing in a variety of roles and suggests that this method of learning can be implemented in a variety of clinical and community settings. The module content can be tailored to meet the needs of a variety of healthcare and allied health disciplines such as medicine, therapy, and social work to reach many professionals. Concise, state-specific clinical practice guidelines regarding ACP, and the development of a state-wide advance directive repository remain important future recommendations.
POSTER
Dockery, H.D. (2016, October). The Development, Implementation, and Evaluation of a Web-Based Learning Module on Advance Care Planning: Enhancing the Knowledge of Clinical and Advance Practice Nurses in Tennessee. Poster session presented at the Tennessee Nurses Association/Tennessee Association of Student Nurses Annual Joint Convention, Murfreesboro, TN.
-
Dr. Osahon Kings Enodunmwenben
Dr. Osahon Kings Enodunmwenben
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Decreasing Inpatient Readmissions in Homeless Patients
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to identify the problem of inpatient hospital readmission at Hennepin County Medical Center (HCMC) Minneapolis, MN, causes of avoidable readmission and create a Quality Improvement (QI) program for key health officials including essential steps in discharge planning, transitional care, follow-up appointments, and long term care.
METHODOLOGY
A quality management tool (Fishbone diagram) was used to identify, explore and display possible causes of inpatient readmissions. A Retrospective Chart Review (RCR) was conducted using Electronic Medical Records (EMR) at HCMC identifying the patients who were readmitted within 30 – 90 days after discharge from January 1st to December 31st 2015. Convenience sampling was used to compare the readmission rates of housed and homeless patients.
RESULTS
There were 20,962 discharges at HCMC between January 1st and December 31st 2015. There were 4262 who had a risk score of 3. The patients with a priority risk score of 3, had a 1063 (25%) rate of readmissions in 2015 and of these admissions 965 were housed and 98 where homeless. Of the housed patients 25% where readmitted within 30 days, while the homeless group had a 29% readmission rate. Overall, the results from the RCR showed that there is no significant correlation between homelessness and inpatient readmissions at HCMC. Although the rate of readmission was four percentage points higher in homeless patients compared to housed patients, the findings was not statistically significant (p = 0.107).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Based on the results, it is important to specifically address the group with extreme risk score (3) who are frequent users of the Emergency Department (EDs). These patients will be the target of our proposed recommendations. In line with the recommendations from the Institute of Medicine (IOM, 2001), to provide patient care that is “safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable”, a quality improvement program was developed that will be disseminated to stakeholders involved in transitional care at HCMC.
-
Dr. Mary Hoft
Dr. Mary Hoft
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Educating First Responders to Identify, Provide Care, and Protect Victims of Human Trafficking
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to increase community first responders’ knowledge and awareness of human trafficking, and improve the ability to identify and respond to the needs of human trafficking victims.
METHODOLOGY
The study was a mixed, quasi-experimental design with a pre-test and 90-minute educational intervention, and included instruction in the use of a screening guide. Three months later post-tests were administered and participant group interviews were conducted.
RESULTS
Quantitative Results: The pre-test mean scores ranged from .5265 to .8395. Post-test mean scores ranged from .6494 to .8395. The within agency means increased between pre- and post-test scores, and increases ranged from .0398 to .1965. The mean score between pre- and post-test scores significantly improved (p < .05) for all but one agency. The pre- and post-test means for the total participants was .5798 and .71968 with a .13928 difference. The paired t-test for total scores was significant at p < .05; total effect size was large (Cohen’s d = 1.084961). Qualitative Results: Themes that emerged from the informal group interviews after post-test completion included: confidence in the ability to recognize trafficking victims, ability to effectively respond to victims, a desire to educate co-workers about human trafficking, a plan to keep the screening protocol available for use in the work setting, change in services to screen for and educate high risk clients about human trafficking, and a desire to collaborate with other participating agencies to develop a coordinated county-wide response to human trafficking
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
This project provided an opportunity for a member of the nursing profession to begin emerging as an expert in human trafficking prevention and highlight the leadership roles advance practice/DNP prepared nurses can assume in this human tragedy that severely impacts the physical and mental health of victims.
-
Dr. Adam Jason Horn
Dr. Adam Jason Horn
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Impacting Inpatient Psychiatric Readmission Rates by Focusing on Subset of High Risk Populations: Determining Characteristics of Subset of High Risk Populations and Releasing Recommendations for Practice
PURPOSE
Readmission rates are being increasingly used as a quality indicator, including possible loss of funding. Psychiatric readmission rates far exceed rates for medical, surgical or maternal/neonatal health readmissions and the local inpatient psychiatric facility in Johnson City, Tennessee exceed the national average. While treatment options are available and effective in reducing readmissions rates for general consumers of inpatient psychiatric treatment, a subset of individuals resistant to traditional interventions exists. This project identifies the characteristics of this subset and develops a protocol for aforementioned facility.
METHODOLOGY
Chart review of the electronic health records of 50 most frequently readmitted to the local inpatient psychiatric facility in Johnson City, TN. Key participants (e.g. discharge planners, prescribers, nursing, administration, etc.) were interviewed for baseline perception of issue. Systems-based, evidence-based treatment recommendations/protocol was developed. Key participants were again interviewed for perception of protocol usefulness.
RESULTS
Protocol developed included increase use of long-acting agents when not contraindicated, admissions to consistent treatment team, brief length of stay defined as two or three day maximum, and referrals to Intensive Outpatient Programs (IOP) available at facility. Key players were overwhelmingly receptive to protocol and conversations regarding implementations
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The results of this study indicate there is a great need and desire for evidence-based guidelines for the reduction of inpatient psychiatric readmission rates among the subset of high utilizers within the psychiatric community. While a significant amount of research has been conducted regarding reduction the reduction of psychiatric readmission rates, little to none has been completed evaluating the subset of high utilizers.
-
Dr. Khairunnissa Aziz Jooma
Dr. Khairunnissa Aziz Jooma
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Educating the Mental Health Providers to become Cultural Competent to identify and provide care regarding Depression in Muslims
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to increase the cultural competency skills of mental health providers and assist them in becoming well equipped in assessing, diagnosing and treating depression in Muslims.
METHODOLOGY
A descriptive study applying two theorists, Dr. Madeleine Leininger’s Culture Care and Diversity and Universality theory, and Dr. Campinha-Bacote Cultural Competent Care Model in a pilot format. A convenience sampling method was used to recruit 25 healthcare professionals as participants. Two tools using pre and post implementation survey was conducted and the data analyzed and presented using descriptive statistics.
RESULTS
For both the assessment tools, there was an increase in the range of 68%-73% from pre assessment to post assessment in the levels of cultural competency and knowledge of beliefs and practices regarding treatment in Muslims with depression. For the IAPCC-R the mean pre-test scores was 69.57 (SD = 8.005) and the post-test score was 74.26 (SD = 8.092), The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test revealed that post-test ranks were statistically significantly higher than pre-test ranks (Z = -2.924; p <.003). Within the constructs of the IAPCC-R, the Wilcoxon Signed rank Test revealed increased scores: Cultural awareness: (Z= -3.200; p < 0.001) Cultural Knowledge (Z=-1.997; p <0.046) and Cultural skill (Z= -2.953, p <0.003). For the MCMHS scale, the mean pre-test scores was 61.32 (SD = 8.132) and the post-test score was 66.32 (SD = 8.839). The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test revealed that post-test ranks were statistically significantly higher than pre-test ranks (Z = -2.653; p < .008).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The findings of this study supports this proponent and highlights the need to educate all mental health providers to become culturally competent in caring of culturally / ethnically diverse population, more specifically focusing on family and community perceptions of mental health and beliefs in treatment when caring for mental illness in Muslims.
Conwill, W.L. & Jooma, K. (2008). Thwarting ethnoviolence against Muslim women: Performing identity in social action. Journal for Social Action in Counseling and Psychology, 1(2), 30-47
-
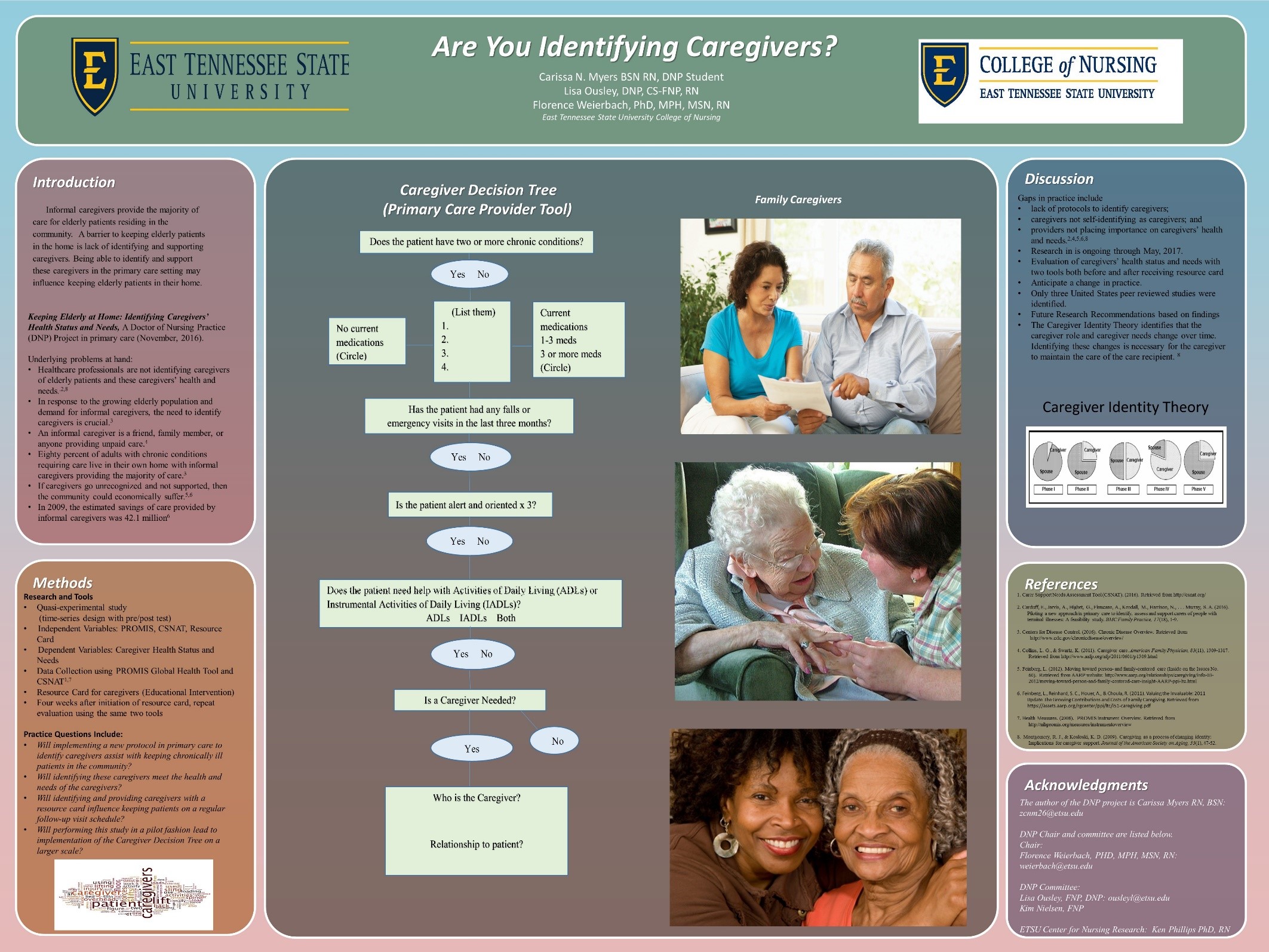
Dr. Carissa Nichole Myers
Dr. Carissa Nichole Myers
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
AGNP
TITLE
Keeping Elderly at Home: Identifying Caregivers’ Health Status and Needs
PURPOSE
Informal caregivers provide the majority of care for elderly patients residing in the community, but these caregivers are not being accurately identified and supported. Identifying caregivers and supporting caregivers may prevent caregiver burden and loss of identity, with a primary goal of keeping the care recipient in the home longer.
METHODOLOGY
A protocol was developed and implemented to identify informal caregivers using a decision tree in a primary care practice. The caregivers’ perceived health status and needs were then addressed using two tools, and the caregivers were provided with a developed caregiving resource card. Follow-up was conducted in four weeks for reevaluation.
RESULTS
A total of 127 elderly patients were screened using the decision tree, 88 did not need a caregiver, 25 needed a caregiver and had a caregiver, and 14 needed a caregiver but did not have a caregiver. Six caregivers consented to being in the study, and five caregivers completed the screening with the intervention and follow-up. All five of the caregivers reported the resource card being useful and providing awareness to unknown resources.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
A new protocol was implemented to assist with identifying and supporting informal caregivers in a primary care setting. Project analysis showed the importance of screening for informal caregivers among this patient population and providing support to these caregivers to ensure the care recipient stays in the home longer. This protocol pilot may be replicated on a larger scale to further evaluate the Caregiver Decision Tree to identify informal caregivers.
POSTER
Myers, C., Ousley, L, Weierbach, F. (2016, October). Keeping Elderly at Home: Identifying Caregivers’ Health Status and Needs. Poster session presented at the Annual TNA-TASN Joint Conference, Murfreesboro, TN
-
Dr. Denise Ruth Spisso
Dr. Denise Ruth Spisso
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Medication Reconciliation Implementation in a Rural Health Clinic
PURPOSE
The purpose of the Doctor of Nursing Practice quality improvement project was to implement and evaluate a systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process in a primary care practice in a rural health clinic in Northeast Tennessee.
METHODOLOGY
Implementation of a systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process in a Northeast Tennessee rural health clinic was the primary aim of the project. The objectives of the project focused on implementation of a defined systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process that was inclusive of all patient contact points within the pilot clinic. The objectives were established to comply with federal reporting and aims, identification of data for medication reconciliation analysis and reporting, and determining project impact on patient total clinic visit times. The project identified medication reconciliation data required for analysis of the clinic and individual provider performance. Clinic performance was based on total provider encounters compared with total provider completed medication reviews and medication reconciliations.
RESULTS
A comparison of 3574 patient encounters with completed medication reconciliations Pre- and post-implementation (79.11% and 87.71%) showed a significant increase of 8.6% (p=0.0001). A time impact analysis revealed that implementation occurred with no significant increase in patient total clinic visit times. The findings led to a quality improvement project that was designed to improve medication reconciliation by improving quality, safety, and efficiency of clinical medication management.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Results of the quality improvement project may be used as a guide when implementing a medication reconciliation process within a rural health primary care clinic. Implementing a systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process inclusive of all patient contact points within a clinic supports a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare.
-
Dr. Ramona Craft Whichello
Dr. Ramona Craft Whichello
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
EL
TITLE
Emotional Intelligence in Nurse Administrators
PURPOSE
Health care organizations face tremendous change and complexity. Nurse administrators must develop skills to build and sustain work environments that promote teamwork and positive patient outcomes. Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to perceive emotions, to access and generate emotions, to understand emotions and emotional knowledge, and to regulate emotions. The study examined pre- and post-EI scores for statistically significant improvement after an EI educational offering and evaluated the relationship amongst RN turnover, RN satisfaction, and Total EI scores.
METHODOLOGY
Nurse Administrators at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) were the population of interest and included individuals with job titles of chief nurse operations and acute care, chief nurse geriatrics and extended care, nurse manager, and assistant nurse manager. A one-group pretest-posttest design purposive sample of nurse administrators (n = 13), using the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) to measure EI before and after an EI leadership development offering.
RESULTS
A branch score for managing emotions was significant (p < 0.05). Pre- and post- total EI, area, branch, and task scores were not significant (p > 0.05). Total pre-EI scores showed a low average level of EI (99.89, 98.86 respectively). RN satisfaction was high and RN turnover was low.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Leadership development opportunities on emotional intelligence (EI) for nurse administrators are important aspect of continued growth. EI can change over time and may have a positive impact on RN satisfaction ad RN turnover.
Whichello, R.C. (2017, April). Emotional Intelligence: Impact on Teamwork. Team Building Retreat for Learning Resource Center Staff, Asheville, NC
-
2017 DNP Graduates
First Column Second Column Erin Elizabeth Bailey
Jamie Boone
Shaquita Lashea Bonds
Mandy Marie Brannen
Leonard Anthony Dinardo
Holly Dillon Dockery
Charles David Edwards
Osahon Kings Enodunmwenben
Theresa Ann Gibbs
Alan Michael Hicks
Nathan R. Hitchcock
Mary Hoft
James Marett HolbrookAdam Jason Horn
Khairunnissa Jooma Aziz
Leslie Moro
Carissa Nichole Myers
Paige Noel Reed
Deana McThenia Rhinehart
Holly Kaimanakea Gyure Sawyer
Ashley Nicole Shouse
Denise Ruth Spisso
Krissa Marie Trombetta
Ramona Craft Whichello
Dorie Wykes
2017 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Susan Adams
Dr. Susan Adams
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
Job Embeddedess of Nurses Working in South Central Appalachia’s North Carolina CountiesPURPOSE
Nurses working in the North Carolina counties of South Central Appalachia (NC-SCA) are a unique subset of nursing professionals. A continued nursing shortage is projected in this area while staffing has improved in other areas of SCA. The purpose of this research was to ascertain the level of job embeddedness of nurses working in NC-SCA in order to offer guidance regarding retention of nurses working in this area.METHODOLOGY
Actively working licensed practical nurses, registered nurses, and advanced practice nurses (nurse practitioners, certified nurse midwives, clinical nurse specialists, and certified registered nurse anesthetists) from 29 North Carolina counties included in South Central Appalachia comprise the study population.RESULTS
Rural Nursing Theory alongside the concept and theory of Job Embeddedness (JE) examines organizational and community influences on retention. Data collection consisted of an online survey and included a demographic questionnaire along with the JE research instrument. Understanding what keeps these nurses on the job is beneficial to nurses, health care organizations, and patients. History of living in rural area, years at job position, intent to stay, work commute in miles, and work commute drive time were significant factors in Job Embeddedess prediction. -
Dr. Angela Collier
Dr. Angela Collier
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
Approachability of Nursing Clinical Instructors: Psychometric Assessment of a ScalePURPOSE
Approachability of nursing clinical instructors is largely unknown and misunderstood, yet critical for millennial students which currently comprise 82% of nursing students (National League for Nursing, 2014). Nursing education consists of both a didactic and a clinical component. Clinical education is dynamic and allows the student an experiential learning opportunity. Therefore, clinical nursing educators are vitally important. Approachability has been identified in many studies as a leading characteristic of an effective instructor. Although the importance of approachability of the instructor is established, currently no scale exists to measure this concept.METHODOLOGY
The purpose of this study was to examine the validity and reliability of the newly developed Approachability of Nursing Clinical Instructor (ANCI) scale.RESULTS
Based on the results of this study, the newly developed ANCI scale meets all four aspects of validity (face, content, construct and criterion-related) and reliability is established. The confirmatory analysis indicated a one-factor scale with 56.102 of the variance explained. There are multiple future recommendations for the ANCI scale which include further psychometric testing the new scale, potential theory testing, education and screening of new clinical instructors and expanding the ANCI within nursing and to other disciplines. -
Dr. Catherine Hebert
Dr. Catherine Hebert
PhD, GCNS-BC, RN
TITLE OF PROJECT
An Exploration of Dementia Friendly Communities from the Perspective of Persons Living with DementiaPURPOSE
The growing global prevalence of dementia coupled with a shift in public perception from a hopeless disease to the possibility of living well with dementia has led to the formation of dementia friendly communities (DFC). DFCs are a new phenomenon in the United States, with a gap in knowledge on input from people living with dementia (PLWD). This study investigated DFCs from the perspective of PLWD in Western North Carolina, with the following research questions:
1. How are interactions and relationships experienced by persons living with dementia in the community?
2. How is community engagement experienced by PLWD?
3. To what extent and in what way is the impact of stigma associated with dementia?
4. What are the attributes of a DFC from the perspective of PLWD?
METHODOLOGY
Eighteen older adults with reported dementia or memory loss were recruited from support groups or community organizations. Semi-structured interviews were conducted in participants’ homes and analyzed using conventional qualitative content analysis.RESULTS
Three major themes emerged from the transcribed interviews (a) transitions in cognition: vulnerable identities, (b) social connections, and (c) engagement in life activities. The dynamic experience of living with dementia revealed by participants suggested the following attributes of a DFC: (a) social inclusion, (b) support for role continuity, (c) availability of meaningful and contributory activities, (d) flexible support as cognition transitions, (e) community dementia awareness (to combat stigma), and (f) a supportive diagnostic process. The presence of care partners in the interviews was supportive, and the evaluation to sign consent tool assisted in determination of participant capacity to self-consent.
The findings were interpreted through the theoretical frameworks of personhood, the social model of disability, human rights and citizenship, the environmental press model, and transitions theory. DFC development requires a contextual lens focused on well-being with input from multiple stakeholders including PLWD. Collaboration among community organizations supported by local, regional, and national policy supporting flexible service provision through cognitive transitions has the potential to provide a strong social network on which to build a DFC.
-
Dr. Kristen Hershey
Dr. Kristen Hershey
PhD, RN
TITLE OF PROJECT
Pre-Licensure Nursing Students' Perceptions of Safety Culture in Schools of NursingPURPOSE
Safety culture has been demonstrated to be a key factor in high-reliability organizations (HROs), yet healthcare has not achieved a safety culture as seen in HROs despite decades of effort. Student nurses are enculturated into their profession during their pre-licensure education. This period offers an excellent opportunity to teach students the values, norms, and practices of safety culture. However, little is known about the state of safety culture in schools of nursing.
The purpose of this study was to examine the state of patient safety culture as perceived by students in pre-licensure nursing programs in the US using a modified version of the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture (HSOPSC).
METHODOLOGY
The School of Nursing Culture of Safety Survey (SON-COSS), the modified instrument created for this study, was administered electronically to a sample of pre-licensure nursing students (N=539) drawn from membership in the National Student Nurses Association (NSNA).RESULTS
The SON-COSS was found to maintain its reliability and validity for use in pre-licensure nursing students. Perceptions of patient safety culture ranged from 81.6% to 23% positive for the 10 dimensions of patient safety culture measured by the SON-COSS. The highest percent positive dimensions for this study were Faculty Support for Patient Safety (81.6%), Teamwork Within Groups (78.3%), and Faculty Expectations and Actions Promoting Patient Safety (68.6%). The lowest percent positive dimensions for this study were Frequency of Events Reported (47.3%), Communication Openness (34%), and Nonpunitive Response to Error (23%). Participants in this study perceived patient safety culture significantly lower for eight of the 10 dimensions measured by the SON-COSS compared to aggregate national data from the HSOPSC (AHRQ, 2016). Only Faculty Support for Patient Safety (81.6%) was significantly higher than the corresponding dimension in the HSOPSC.
The results of this survey indicate that students recognize the importance of safety to their faculty, but they do not perceive the presence of a just culture, an essential prerequisite for a culture of safety. This study provides a reliable and valid instrument to measure safety culture in schools of nursing and baseline data to understand the state of safety culture in this population.
-
Dr. Barbara Jared
Dr. Barbara Jared
PhD, MSN, RN, WHNP-BC
TITLE OF PROJECT
The Impact of Teach-Back as a Patient Education Tool in Women with Inadequate Maternal Health Literacy Seeking Immunizations for their ChildrenPURPOSE
Health literacy is recognized as a contributor to health outcomes and maternal health literacy is important to the health and wellbeing of children and families. Of particular interest are mothers seeking immunization services for their children. The complexity of the recommended immunization schedule and the care management of children receiving immunizations have the potential to create negative health outcomes in the low health literate population. Assessment of maternal health literacy and provision of effective patient education adapted to the health literacy level of the individual is important for information transfer. The Teach-Back provides an opportunity to both assess understanding and reinforce teaching.METHODOLOGY
This study used an experimental design to study two groups of women for a total of 90 participants in a public health department setting. The control group received the usual immunization patient education using Vaccination Information Sheets. The intervention group also received patient education in this manner plus use of the Teach-Back. Immunization knowledge was assessed prior to and after patient education. Immunization currency was assessed as well.RESULTS
The Newest Vital Sign was used to assess the maternal health literacy for 90 mothers bringing their children for immunizations. A demographic survey addressing both individual characteristics and social determinants of health variables was also administered.
Most of the participants were low health literate (84%) and low health literacy was related to lower immunization knowledge and poor immunization currency. Social determinants of health variables were related to maternal health literacy, immunization knowledge and immunization currency. The results demonstrated an improvement of immunization knowledge scores with the use of the Teach-Back method of patient education.
Additional research is needed in the area of patient education interventions specific to the low health literate population. The development of instruments to measure interactive and critical health literacy are needed and interventions to promote growth in health literacy are also needed. Clinically, improved patient education interventions for low health literate mothers has the potential to improve health outcomes and decrease health care costs of these women, their children and their families.
-
Dr. Barbara Maria Rauscher
Dr. Barbara Maria Rauscher
PhD
TITLE OF PROJECT
The Perceptions of Success of Latino Nursing School Graduates In the Appalachian Region of the United StatesPURPOSE
This research study addressed the perceptions of success of Latino nursing school graduates in the Appalachian region of the United States. Understanding the reasons for success of Latino nursing students is important because the success of these students will add to the diversity of the nursing workforce. This is an issue which gained the attention of nurse leaders and nurse educators with the Sullivan Report (2004).METHODOLOGY
This narrative descriptive study provided analysis of interviews with nine Latino nursing school graduates. Participants were recruited via social media, contacts with schools of nursing, and the snowball effect. A total of fourteen interviews were conducted. Participants and their families immigrated from Brazil, Costa Rica, Cuba, and Mexico. Participants attended school in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee.RESULTS
Interviews revealed themes of Familism, Empowerment, and Perseverance. Familism was an overriding theme throughout the interviews. The theme of Empowerment was supported by descriptions of parental sacrifice, parental and family support, and support of faculty. Perseverance was displayed in multiple ways by participants. One of the most compelling was their need to honor their family. Another area which fueled their perseverance was faith. Lastly, participants stated that their need to be self-sufficient added to their perseverance. Self-efficacy surfaced as an attribute they all attained.
2016 PhD Student Dissertations
-
Dr. Rebecca L. Turpin
Dr. Rebecca L. Turpin
PhD, MSN, RN, NEA-BC
TITLE OF PROJECT
Psychometric testing of the Presence of Nursing Scale: Measurability of patient perceptions of nursing presence capability of nurses in an academic medical center.PURPOSE
Nursing presence occurs when nurses expend themselves on the behalf of a unique patient. This phenomenon requires further research to develop instruments. The Presence of Nursing Scale (PONS) measures the patient’s perspective (Kostovich, 2012). Psychometric testing of PONS-Revised using exploratory factor analysis is warranted to further develop a reliable and valid measure of nursing presence. Contextual workplace variables need exploration in inpatient settings for correlation with nursing presence.METHODOLOGY
A convenience sample of 122 adult inpatients from ten acute-care nursing units in a Southeastern Magnet hospital were surveyed to conduct the first psychometric testing of this revised instrument using exploratory factor analyses. Seven research questions evaluated potential correlations between the PONS-R, patient satisfaction using nurse-sensitive measures of HCAHPS, nursing unit-specific workforce factors and patient demographic factors.RESULTS
PONS-R demonstrated high internal consistency reliability (r = .974), test-retest reliability (statistically significant at the .01 level) and divergent validity (p=.002). PONS-R compared to nurse HCAHPS measures was statistically significant at the .01 level, (r = .736). EFA revealed one factor (eigenvalues over 1), with a weak secondary factor centered on intimacy factors suggesting addition of items and repeated study with a larger sample size to further psychometrically develop the instrument. Unexpected negative correlations were found with unit-workforce factors including average RN experience level (r= -.185, significant at the .05 level), and average RN age (r = - .218). An unexpected positive correlation was found - percentage of Associate degree nurses (r = .269, statistically significant at the .05 level. The Triangle region was correlated with a higher PONS-R score (p = .038; n=4), otherwise no statistically significant correlations were found for PONS-R and patient demographics nor patient-specific variables such as estimated number of RN providing care, nor length of stay on the unit.
Further psychometric testing is indicated with larger samples and perhaps with the inclusion of intimacy factor items. Additional correlational studies focused on other patient quality outcomes measures with expansion of nurse demographics is indicated to explore for confounding variables.
2025.04.10..01 v. 43 | Associate Dean for Research
 Stout Drive Road Closure
Stout Drive Road Closure