PhD Student Dissertations
2022 DNP Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Marie Julie Boudreau-Klymas
Degree:
DNP
Degree Concentration:
Nursing Healthcare Leadership
TITLE
Integrating American Heart Association’s Self-Check Plan in Creating a Standardized Heart Failure Patient Education Program
PURPOSE
This quality improvement project aims to assess the effectiveness of integrating the AHAs’ Self-Check Plan (the tool) in creating a standardized HF patient education program to reduce 7-day and 30-day readmissions.
METHODOLOGY
The tool was integrated in the existing HF patient education program as one step in standardizing the content. Introduction of the tool was performed after unit nurses initiated basic HF patient education. A HF-NC (HF-nurse coordinator) reviewed the tool correlating early self-initiated strategies within the green, yellow, and red sections with the specific early signs and symptoms of decompensation experienced by the patient, promoting the early activation of interventions mitigating further decompensation and need for readmissions.
RESULTS
A total of 61 of 187 patients were exposed to the standardized HF patient education tool (AHA+). Participants average age was 67 years old, 94% presenting with NYHA Class III C, 3% Class IV, and 3% Class I or II. There was no change in overall pre- and post-interventional 7-day and 30-day HF readmission rates. However, significant 7-day readmission reduction from 8% to 2% (4/187) were achieved in the AHA+ patients.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Results reflect the importance of systems thinking, and the intentional strategic operationalization of transition of care programs for patients with complex chronic disease management. Fragmented care, poor communication, and programmatic implementation significantly limit the achievement of outcomes of scale.
-
Dr. Jacqlyne Bowman
Dr. Jacqlyne Bowman
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Implementation of evidence-based practices to improve follow up care following an inpatient hospitalization
PURPOSE
Persons hospitalized for mental health conditions are frequently lost to follow up after discharge. Lack of client involvement and transportation are barriers to follow up attendance. The purpose of this quality improvement project was to increase attendance to follow up appointments after an inpatient mental health hospitalization.
METHODOLOGY
A discharge questionnaire was utilized by case managers and clients in a mental health hospital that assessed for barriers to follow up care (n=612).
RESULTS
Female clients were more likely to attend their follow up appointments when the questionnaire was utilized (p<0.001). Follow up attendance increased from 49 to 56 percent. Transportation was required by 28 percent of clients in the inpatient setting.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The development of the discharge questionnaire allows for a streamlined discharge process between the case manager and client. This provides a potential solution to inadequate discharge education.
Bowman, J.W. (2022). Implementation of evidence-based practices to improve follow up care following an impatient hospitalization. Podium presentation presented at East Tennessee State University Appalachian Research Symposium, Johnson City, TN.
-
Dr. Jacklyn Halpin
Dr. Jennifer Cooke
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Medication Reconciliation in Primary Care
PURPOSE
Patients in primary care are experiencing high levels of adverse drug reactions due to inaccurate or incomplete medication reconciliation practices. If inadequate medication reconciliation practices continue, the healthcare status of patients will decline. Medication reconciliation is a responsibility of clinicians, prescribers, pharmacists, and patients. The purpose of this quality improvement project is to improve the medication reconciling practices in primary care thus preventing adverse drug events
METHODOLOGY
This medication reconciliation quality improvement project was implemented in a rural primary care clinic in eastern Tennessee. The goal of the planned intervention was to improve the medication reconciliation process by utilizing an evidenced based instrument called the Medication at Transitions and Clinical Handoff (MATCH) tool. The MATCH tool serves as a reconciling tool for patients and aides in decreasing medication errors and adverse events in the clinical setting.
RESULTS
During the 4-week project implementation period 220 patients were seen. The final number of patients’ who participated in the project were (N=88). 55 percent female, 44 percent the sample were female who made up 55 percent of the population, the male population followed with 44 percent. Age ranges measured in the study ranged from 31-60 being the most affected group at 55% overall. An average of 2.56 medication discrepancies per participant was identified with (N= 88) patients’ (SD= 2.435). The discrepancies found in female population had a mean of 2.80 (SD= 2.598) and the mean male discrepancies was 2.26 (SD= 2.209). Based on the Levene’s Test for Equality, the significance of the two-sided p-value was 0.0304, resulting in there being no significance found in the number of discrepancies.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Improving medication reconciliation has the potential to decrease adverse drug events and maintain patient safety in the primary care setting.
-
Dr. Kaitlin Holley
Dr. Kaitlin Holley
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Women’s Health Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Implementation of an Insulin Resistance Patient Education Toolkit in Reproductive-Age Females
PURPOSE
The purpose of this quality improvement project is to improve access to insulin resistance education in reproductive-age females through the use of an evidence-based online toolkit.
METHODOLOGY
Quantitative data collected included deidentified data such as age, ethnicity, International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10), and insulin resistance risk criteria met. Qualitative data collection included a staff feedback survey administered via REDCap, a secure online survey database. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics within Excel and displayed in bar graphs and pie charts.
RESULTS
Of 16 female patients aged 15-49 (n=16) who met the risk criteria for insulin resistance and received the toolkit, 69% of the sample (n=11) followed the Instagram account (became new subscribers to the account to view posts in their feed). Staff feedback surveys revealed 100% of staff reporting ease of use, timesaving, cost-effective, and likeliness to use as supplemental patient education in the future.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
This project demonstrated the ease of use, cost-effectiveness, and time-effectiveness of an evidence-based online toolkit for patients with insulin resistance. A high Instagram follow rate of 69% and a high engagement rate of 64% confirms that reproductive-age females are seeking information from this social media platform and value the educational content of the online toolkit. The online Instagram account also increased accessibility to resources in a rural, underserved community. Implications for future practice are that evidence-based patient education through smartphone technology may be an effective approach to knowledge dissemination in reproductive-age females with insulin resistance especially in rural areas. To improve access to evidence-based insulin resistance education, healthcare providers should screen at-risk patients and provide online resources such as this toolkit.
Holley, K. (2022, July). Implementation of an Insulin Resistance Patient Education Toolkit in Reproductive-Age Females. Poster session presented at East Tennessee State University Conference, Johnson City, TN. https://etsu.hosted.panopto.com/Panopto/Pages/Viewer.aspx?id=f7ace3ba-49f1-48d2-a7c3-aed601179080&start=939.183043
-
Dr. Sandra Marshall
Dr. Sandra Marshall
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Best Practices: Antibiotic Stewardship and the Implementation of Evidence-Based Guidelines During Upper Respiratory Infections Among Rural, Primary Care Patients
PURPOSE
The purpose of this quality improvement (QI) project was to implement antibiotic-prescribing guidelines for URIs, clinic-wide education, and antibiotic stewardship (AS). The aim was to reduce antibiotic overuse.
METHODOLOGY
This QI project was conducted at a rural, family practice clinic. Participants included the nurse practitioners and office staff who cared for adult patients, ages 18 and up, who presented with upper respiratory symptoms. The American Academy of Family Physicians’ URI antibiotic-prescribing guidelines were used to compare antibiotic prescribing practices pre- and post-intervention. This initiative included a provider education session and educational videos, posters, and scientific literature. The Knowledge-to-Action framework was used to translate research into practice and data was collected through the administration of questionnaires and the review of EMRs.
RESULTS
The results indicated that the interventions were effective in reducing the number of unnecessary antibiotics prescribed for upper respiratory-related illnesses. Additionally, the findings illustrate patient preferences, outside of guidelines, influence prescribing behaviors.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
This QI initiative was driven by a need to improve practice and educate patients, staff, and providers regarding AS for upper respiratory-related illnesses. The evidence correlates with previous research and demonstrates that interventions such as clinic-wide education, implementation of guidelines, and identification of barriers and facilitators are all vital components of AS. In addition, it implies that patient partnering in AS education is imperative. This initiative may present likely implications for future research in antibiotic practice trends and the tailoring of antibiotic use.
Johnson, S. K. (2022, April 14). Best Practices: Antibiotic Stewardship and Evidence-Based Guidelines During Upper Respiratory Infections Among Rural, Primary Care Patients. Poster session presented at Epsilon Sigma at-Large Chapter Research Day 2022, Morristown, TN.
-
2022 ETSU DNP Graduates
Jessica Altman
Mary Ameh
Julie Boudreau-Klymas
Jacqlyne Bowman
Courtney Burleson
Kaitlynn Earls
Alicia Emery
Danielle GilesJacklyn Halpin
Grace Herriman
Sukesh Jadav
Carmen Jones
Sandra Marshall
Brittany Mendo
Stephanie Sossong
Tessa Woodroof -
2022 ETSU TTU Joint Program DNP Graduates
Laura Allen
Amy Burse
Kayla Foster
Heather Cathey
Kaitlin HolleyShawn Malugin
Kelly Marcum
Anna Oprisch
Melanie Stanton
Marlena Wright
2021 DNP Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Virginia Bradley
Dr. Virginia Bradley
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Promoting AIMS for Tardive Diskinesia: A Program Evaluation
PURPOSE
To ascertain the effects of an updated procedure and screening for tardive dyskinesia (TD) with the Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) after initiation of the scale in the electronic medical record (EMR).
METHODOLOGY
Data included patient encounters of patients taking the most frequently prescribed antipsychotics between August 19 and November 26, 2020. All other encounters were excluded. Deidentified data were extracted from the EMR onto an Excel spreadsheet and transferred to SPSS for analysis.
RESULTS
Of 2167 patient encounters (N=2167, n=853), 108 (12.6 %) AIMS forms were completed. The analysis showed that varied provider types completed the AIMS forms, with the NP having the highest adherence rate (46.3 %), MDs had the lowest rate (14.8 %).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Results indicated a need for ongoing education, revised rating scales, and ongoing program evaluations. Improvement suggestions for similar evaluation projects include data analysis showing all prescribed AP-meds and a more complete incorporation of the entire procedure to show prescribing rationale, clinical diagnosis, comorbidities, and screening rationale.
Bradley, V.F., & Weierbach, F. (2021, April). AIMS screening: A procedure evaluation. Poster session presented at East Tennessee State University Conference, Johnson City, TN. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nZg9jOfI0aE
Bradley, V.F., & Weierbach, F. (2021, April). AIMS screening: A procedure evaluation. Poster session presented at East Tennessee State University Conference, Johnson City, TN.
-
Dr. Jennifer Cooke
Dr. Jennifer Cooke
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Implementing A Brief Tobacco Cessation Intervention in Primary Care: A quality Initiative Project.
PURPOSE
The purpose of this quality improvement (QI) initiative was to implement a brief tobacco cessation intervention, such as the 2 A’s and R, into a primary care clinic. The primary outcome was to measure program implementation by nurses. A secondary outcome was measured to see if the implementation of the 2A’s and R screening tool in the primary care clinic improved the number of referrals for smoking cessation treatment.
METHODOLOGY
The design of this project was a QI initiative. As part of the initiative, an educational in-service on using the 2 A’s and R of smoking cessation was presented to the clinical nurses. During the implementation period, clinical nurses recommended the intervention to the known tobacco smokers who accessed the clinic. The nurses then offered a referral to be seen by a primary care provider to discuss smoking cessation or the patient was advised to contact the Tennessee (TN) Tobacco Quitline.
RESULTS
From the 903 patients who accessed the clinic, 44% (n=402) of patients were screened for smoking status. Only 15% (n=61) of patients identified as tobacco users, and from those, 69% (n=42) were not ready to quit, 18% (n=11) were ready to quit and received the Quitline information, and 13% (n=8) stated that they were not ready to quit but requested the Quitline number. None of the patients screened accepted a referral to schedule an appointment to receive smoking cessation.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
This project supports the goal of Healthy People 2030 of delivering a smoking cessation intervention to address health promotion in all persons. Delivering an evidence-based brief tobacco intervention by nurses, provides an exceptional opportunity to increase awareness of tobacco's effects on health. Empowering nurses with health promotion training can boost confidence to provide the intervention that will reach countless patients.
Cooke, J., Short, C., Hemphill, J. (2021, April 7). Implementing A Brief Tobacco Cessation Intervention in Primary Care: A quality Initiative Project. (Poster Presentation). [Virtual conference session]. Epsilon Sigma at- Large Research Day, Johnson City, TN, United States. http://www.etsu.edu/nursing/research/epsig_research_day.php
-
2021 DNP Graduates
Virgina Faye Bradley
Richard G. Brewer, III
Jennifer Marie Cooke
Beth Ann Watts Cruz
Hope Elizabeth Diaz
Elizabeth T. Sparks
Rebecca Lynn Turner
2020 DNP Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Rebecca T. Clark
Dr. Rebecca T. Clark
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Monitoring Prediabetes Screening in Two Primary Care Offices in Rural Appalachia: A Quality Improvement Project
PURPOSE
Prediabetes is major risk factor for the development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). One-third of the population in the United States has prediabetes, but 90% remain undiagnosed because healthcare providers are not performing screenings. The purpose of this process improvement project was to implement prediabetes screening, prediabetes identification, and a referral process to a registered dietician/certified diabetes educator (RD/CDE) in two Federally Qualified Health Centers.
METHODOLOGY
This was a quality improvement project conducted over a six-week period after receiving approval from the University’s Internal Review Board. The risk assessment tool was the “Are you at risk for Type 2 Diabetes?” Evidence-based treatment interventions included referral to a RD/CDE, education on 5%-7% total body weight loss, and/or 150 minutes of exercise per week. The screening results and interventions data were coded, extracted into SPSS Version 25, and analyzed. Aggregate data reported patient characteristics, quantity of screenings performed, evidence-based recommendations offered, and patient risk factors for prediabetes.
RESULTS
The percentage of patients at risk for prediabetes was 41.3% (n=111). The most frequent risks were identified as overweight, history of hypertension, family history of T2DM, and older age. Providers offered education on weight loss 68.5% (n=76) and exercise 76.6% (n=85) but referred 33.3% (n=37) patients for nutrition education. The screening rates were 52.3% (n=176) and 72.5% (n=244) in clinics A and B respectively. A gap remains in using evidence-based recommendations to decrease risk of prediabetes. Prediabetes screening identified a greater percentage of persons in this population.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Consistent implementation of prediabetes risk assessment and following evidence-based interventions would positively impact patient outcomes. Providing appropriate education and resources will aid healthcare providers in preventing chronic disease. This project can be easily implemented to identify persons at risk for prediabetes.
Clark, T., Mullins, C.M., & Hemphill, J. (2020, April 21-22). Monitoring Prediabetes Screening in Two Primary Care Offices in Rural Appalachia: A Quality Improvement Project. (Poster Presentation). Appalachian Student Research Forum, Johnson City, TN, United States. https://www.etsu.edu/studentresearch/ (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
-
Dr. Georgiana C. Hogan
Dr. Georgiana C. Hogan
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Constipation in the Long-Term Care Resident
PURPOSE
An evidence-based clinical practice guideline was developed to prevent and manage constipation in the long-term care (LTC) resident.
METHODOLOGY
A literature review was completed, and evidence was evaluated and included into the initial draft recommendations. The guideline was reviewed for content validity using a Delphi Committee of clinical experts in gastroenterology, geriatrics, and pharmacy. The updated guideline was presented to an interdisciplinary team of long-term care residents. Participants were asked to review and complete a survey regarding clinical applicability of the guideline. Finally, the guideline was evaluated by a group of Doctoral prepared practicing nurse practitioners using the AGREE II instrument.
RESULTS
Thirty-one interdisciplinary members participated in the education session and 30 surveys were received. Overall, the interdisciplinary team members agreed or strongly agreed the guideline was clinically applicable. The AGREE II appraisers aggregated scores were 85% or higher in every domain, indicating the guideline is high in quality.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The information from the guideline highlights several clinical pearls. The goal should be regular bowel movements, avoid periodic cleanouts. Do not use milk of magnesia or magnesium citrate with the LTC resident. They are contraindicated in those with renal impairment, congestive heart failure, electrolyte imbalance, risk for dehydration, and hypertension. Do not use enemas or soap suds buckets. These medications may result in perforation, electrolyte imbalances, renal failure, sepsis, and death (<4%). Use the digital rectal exam to assess constipation, especially to assess for fecal impaction. Fecal impaction can lead to severe morbidity and mortality, consider admission to the Emergency Department. Add more prunes and fiber. Hospitalization can lead to constipation. Do not discontinue scheduled bowel medications. Prescribe the max dosage of bowel medication before attempting another medication.
Hogan, G.C. (2020, April). Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Constipation in the Long-Term Care Resident. (Poster Presentation). The Charles George VA Medical Center Community Living Center, Asheville, NC, United States.
Hogan, G.C. (2020, April). Guideline for the Prevention and Management of Constipation in the Long-Term Care Resident. (Podium Presentation presented to the Charles George VA Medical Center Interdisciplinary Team, Asheville, NC, United States.
-
Dr. Rhonda Morris
Dr. Rhonda Morris
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Family Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Advance Care Planning in Primary Care: Evaluation of the Conversation Starter Toolkit Implementation
PURPOSE
Advance care planning is a standard of care designed to help patients understand illness progression, anticipate outcomes, and to plan for the last stages of life. Despite three decades of demonstrated benefits in the United States, advance care planning still has not become routine practice and only one-third of adults have advance directives. Primary care clinicians provide care throughout long-standing relationships with forty-five million Americans who are living with chronic illness. The purpose of this project was to enhance the number of patient-provider advance care planning discussions, leading to patients making informed decisions about advance directives.
METHODOLOGY
This was a quality improvement project where providers initiated the Conversation Starter Kit for patients presenting for Medicare Annual Wellness Visits in a rural primary care setting in the Southeastern United States. Aggregate data was collected from the electronic health record by the clinic staff to include the number of patients with existing advance directives, the number of advance care planning conversations documented, and the number of Conversation Starter Kits documented pre- and post-implementation. Inclusion criteria were Medicare or dual-eligible patients aged 50 years or older presenting for a Medicare Annual Wellness Visit. Exclusion criteria were patients less than 50 years old or those presenting for a visit other than a Medicare Annual Wellness Visit.
RESULTS
The providers’ advance care planning discussion documentation increased by 6.7% and the providers’ advance directive documentation increased by 9.5%. Integrating the Conversation Starter Kit into Medicare Annual Wellness Visits in a primary care practice increased and opened up provider-patient conversations for end-of-life care planning.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Improving advance care planning discussion leads to patients making informed decisions about end-of-life care.
Morris, R., Mullins, C.M., & Sargsyan, A. (2020, April 21-22). (Poster Presentation). Appalachian Student Research Forum, Johnson City, TN, United States. https://www.etsu.edu/studentresearch/ (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
-
Dr. Nancy Sciara
Dr. Nancy Sciara
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Adherence to Perinatal Depression Screening Guidelines: A Retrospective Review
PURPOSE
The purpose of the project was to evaluate adherence to depression screening guidelines with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), in a rural obstetrics and gynecology practice in North Carolina. The project aims were to: (a) conduct a twelve month retrospective chart review to quantify the number of completed screens, (b) determine the number of positive screens, (c) determine if referrals were made for positive screens, and (d) disseminate recommendations based on project outcomes.
METHODOLOGY
Through electronic medical records review, appointments were evaluated to determine when patient visits occurred, then the charts were reviewed on the specific date to determine if the PHQ-9 was completed. If the screening was completed, the screening score was obtained, and provider notes were reviewed to determine if the patient was referred for further treatment.
RESULTS
The data (N= 1859) were analyzed in Excel by month, visit type, score result, and presence of referral when indicated. During new OB visits, depression screens were completed 23% of the time and for the postpartum visits, the completion rate was 67%. Cumulatively, depression screens were completed at 44% of the perinatal visits. Referrals were offered at 12% rate with positive depression screening results. Findings of the project indicated that screening and referral were inconsistent. There were times when screens were completed, with positive results for depression however documentation did not indicate that there was discussion between patient and provider. Additionally, there was lack of documentation when the patient indicated on the screen that she “would be better off dead”.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The findings of this project indicated a need for policy creation to streamline consistent screenings. Educating the clinical staff and providers regarding the PHQ-9, communication of screening scores, and importance of referral to a mental health provider will improve patient outcomes.
Sciara, N. (2020, April 20-21). Adherence to perinatal depression screening guidelines: A retrospective review [Conference session]. Appalachian Student Research Forum (ASRF), Johnson City, TN, United States. research@etsu.edu (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
Sciara, N. (2020, April 3). Adherence to perinatal depression screening guidelines: A retrospective review [Conference session]. Epsilon Sigma at-Large Research Day, Morristown, TN, United States. stephanie.conder@lmunet.edu (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
-
Dr. Drew S. Turner
Dr. Drew S. Turner
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner
TITLE
Evaluation of a Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper and Referral Protocol
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project is to evaluate the effectiveness of a mental health toolkit: the Tennessee Suicide Prevention Network (TSPN) Suicide Behavior Procedure Checklist. To address teachers’ and staff members’ knowledge of suicide prevention, an evidence-based suicide prevention gatekeeper training program called Question, Persuade, Refer (QPR) was implemented.
METHODOLOGY
This Quality Improvement Project is designed as an effort to help generate a sustainable change in suicide monitoring practices at a private, Christian school located in the Northeastern part of the United States. Step 1: Provide suicide prevention gatekeeper training by Question, Persuade, Refer (QPR) Gatekeeper Training. Used a pre-test, post-test, and six weeks post retention test to monitor teachers and staff members knowledge level on suicide prevention. Step 2: Education provided on the TSPN Suicide Behavioral and Procedural Checklist and Mental Health Toolkit. Step 3: Monitor the number of students at risk of suicide and use of the toolkit.
RESULTS
The increase in knowledge was significant when comparing the pre-test to the initial post-test (p<0.001) and the six-week post-retention test (p<0.001). Three students were identified at risk of suicide during an 8-month monitoring period. Resources from a mental health tool kit were tracked also.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Based on the findings, it is recommended that similar programs be implemented in schools to reduce the rate of adolescent suicide.
Turner,D. (2020, April 21-22). Evaluation of a Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper and Referral Protocol (Poster Presentation). Appalachian Student Research Forum, Johnson City, TN, United States. https://www.etsu.edu/studentresearch/ (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic)
Turner,D. (2020, March 26). Evaluation of a Suicide Prevention Gatekeeper and Referral Protocol (Podium Presentation). Tennessee Suicide Prevention Network Northeast Regional Meeting, Johnson City, TN, United States https://www.tspn.org (Conference Canceled due to COVID-19 Pandemic).
-
2020 DNP Graduates
Anaya Baeza
Melanie Greer
Barbara Hayes
Shenia Johnson
Rhonda Morris
Nancy Sciara
Leslie Trivett
Melissa WellsRebecca Terrie Clark
Angela Harless
Georgiana Hogan
Shayla Kilgore
Vickie Pitman
Adriana Smith
Drew Turner
Marah Wise
2019 DNP Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Karen L. Burchfield
Dr. Karen L. Burchfield
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
Executive Leadership
TITLE
Evaluation of Lean Standard Work Methodology to improve Medication Administration Record Completion in an Urban Elementary School System
PURPOSE
Enhance completion of medication administration records (MAR) in school systems.
METHODOLOGY
Post-intervention data was collected from the four schools and provided to evaluate as either complete or incomplete as a whole. One school did not have incomplete MARs before or after implementation of the intervention. Therefore, statistical analysis was conducted on data from only three schools, using the Chi-square test. Two of the three schools demonstrated a significant decrease in incomplete MARs after the intervention and the overall improvement was 34.1%.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Follow nursing professional bodies position statements and recommendations for establishing policies and procedures for medication administration to include MAR completion.
-
Dr. Joseph Harris
Dr. Joseph Harris
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Improvements in Addressing Patient Smoking Status on an Assertive Community Treatment Team by Implementing the Five A’s of Smoking Cessation
PURPOSE
The risks of tobacco use are especially problematic in patients with severe and persistent mental illness (SPMI), yet any Assertive Community Treatment Team (ACTT) staff members were not addressing patient smoking status. The purpose of this quality improvement project was to assess the ACTT’s adoption of a new program grounded in the 5 A’s of smoking cessation and to enhance ACTT staff knowledge regarding smoking cessation and tobacco cessation myths.
METHODOLOGY
The rate in which ACTT staff addressed smoking with patients was compared for the four weeks prior to an educational intervention and for 12 weeks post-intervention. ACTT staff also completed an anonymous pre- and post-intervention survey to measure any changes in perceptions and knowledge about smoking cessation. Descriptive statistics were utilized to analyze the data.
RESULTS
The percentage of visits in which staff addressed smoking increased from 4.6% to 12.0% post-intervention and patients were referred to the quitline. There was also a reduction in the acceptance of tobacco cessation myths and increased knowledge and confidence that patients with SPMI can quit smoking.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The smoking cessation program improved staff knowledge related to smoking cessation, equipped staff with resources to help patients to quit smoking, reduced the acceptance of tobacco cessation myths, and facilitated most staff members (70%) to assist patients to quit smoking during the project. Patients with mental illness are interested in quitting smoking and are more apt to do so when health professionals are encouraging them to quit smoking. Nurses who adopt a strong position on smoking cessation can act as champions of change when executing smoking cessation programs.
-
Dr. Pamela Ann Trent
Dr. Pamela Ann Trent
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
The Effects of Nurse-Initiated Protocols on Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Outcome Measures in the Emergency Department
PURPOSE
Annual emergency department (ED) visits continue to rise, increasing the risk for prolonged wait times and negative consequences. This necessitates innovative approaches to improve efficiency and outcomes. The use of nurse-initiated protocols upon patient arrival to the ED expedites care through prompt ordering and completion of diagnostic tests. In turn, throughput and departmental performance measures linked to efficiency and reimbursement may be improved. The purpose of this project was to evaluate the effects of nurse-initiated triage order sets on Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services outcome measures for discharged patients.
METHODOLOGY
De-identified, aggregated data specific to reportable outpatient outcome measures in the ED was collected over a three-month period (N=92) in 2018 and compared to data of the same time frame in 2017. The efficiency-related outcome measures included median time from ED arrival to ED departure for discharged ED patients (LOS), door to diagnostic evaluation by a qualified medical professional, left without being seen (LWBS) rate, and nurse use of standing order sets.
RESULTS
The number of nurse-initiated protocols increased significantly during the study period (Z = -2.31, P = 0.02). A statistically significant decrease was found in the LOS of discharged patients (Z = -2.33, P = 0.02) and door to provider evaluation time (Z = -9.66. P < 0.01). There was a non-significant decrease in the LWBS rate (Z = -0.72, P = 0.48).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
A relationship exists between the use of protocols and clinically and statistically significant improvements in ED performance measures. It is likely that protocols may benefit emergency departments by reducing ED overcrowding, improving throughput, and increasing reimbursement through CMS-related value-based purchasing models. In turn, patient outcomes may be improved by mitigating the negative effects of prolonged ED wait times.
-
2019 DNP Graduates
Afolake Awolaja
Rony Boe
James Coombs
Joanna Dymora
Bupe Habiyambere
Joseph Harris
Ashley Lockhart
Kendra O’quinn
Pamela Trent
Mathew WoodJulia Blocker
Karen Burchfield
Hanna Crawford
Rebecca Garrett
Tonia Hale
Ryan Kerrins
Jill Newton
Latisha Toney
Lisa Waye
2017 DNP Scholarly Projects
-
Dr. Erin Elizabeth Bailey
Dr. Erin Bailey
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
BSN-DNP Perceptions of the DNP Essentials and How They Apply to Future Advance Practice Roles
PURPOSE
Researchers throughout available literature have shown growth in DNP programs, positive perceptions of the DNP degree, and DNP graduates struggling to actualize DNP education to practice. However, BSN-DNP students’ perceptions of the foundation of the degree have not been assessed. The purpose of this study is to explore BSN-DNP students’ perceptions of the DNP Essentials, upon which the program is based, and how they see the Essentials apply to their future advanced nursing practice roles. The study is informed by Benner’s (1982) theory of Stages of Clinical Competence.
METHODOLOGY
A qualitative descriptive study design was used and sample participants were full-time students at a state university’s BSN-DNP program in the southern region.
RESULTS
The findings from the data analysis show three themes emerging around the general concept of Becoming a DNP, which included Uncertainty of Role, Preparation for Role, and Values of Role.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Implications of the findings provided insight into the perceptions of BSN-DNP students on the DNP Essentials and how they will be applied to future practice. The findings inform DNP faculty regarding students’ understanding of the Essentials and how to better connect the Essentials to practice.
-
Dr. Mandy Marie Brannen
Dr. Mandy Marie Brannen
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Improving Health Outcomes for Mother and Baby through PCP Education
PURPOSE
Postpartum depression is a serious mental illness that can have negative consequences to the mother and baby. Depression screening takes place at prenatal and postpartum visits; however, subsequent follow-up rates for mental health care is lacking. This project assessed primary care providers’ perceptions, knowledge, interventions, and barriers associated with postpartum depression.
METHODOLOGY
A pre-experimental pre-test post-test design was used to assess primary care providers working with pregnant women, and up to 12 months postpartum. Providers were employed at a federally qualified health center and were assessed on the topic of depression. A four-point Likert scale was utilized with the highest value indicative of the most positive response. An evidence-based educational intervention, given by a clinical expert on perinatal mood disorders was followed by the post-test questionnaire. Data was analyzed with the Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test.
RESULTS
Findings suggest that providers have a more positive response about knowledge, interventions, and barriers associated with postpartum depression following an educational intervention. Additionally, mental health care follow-up rates increased from 10% to 12.5% following the educational intervention.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Quality improvement efforts involving evidence-based educational interventions on postpartum depression, given to primary care providers, may assist in improving health outcomes for both mother and baby.
-
Dr. Holly Dillon Dockery
Dr. Holly Dillon Dockery
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
AGNP
TITLE
The Development, Implementation, and Evaluation of a Web-Based Learning Module on Advanced Care Planning: Enhancing the Knowledge of Clinical and Advance Practice Nurses in Tennessee
PURPOSE
The use of a web-based learning modules has been suggested as a way to reach out to healthcare professionals to improve the processes surrounding Advanced Care Planning (ACP) for adults with chronic conditions. The purpose of this project is to develop, implement, and evaluate an ACP educational program for clinical nurses and advance practice nurses in Tennessee.
METHODOLOGY
The program is guided by the PRECEDE-PROCEED model, which has been shown to be effective for healthcare education. The non-experimental design included a needs assessment, personal profile/demographic survey, an educational intervention in the form of a web-based learning module with associated pre-post-tests, and program evaluation.
RESULTS
71 responses were received from an electronic needs assessment survey and 21 participants were recruited for program completion. Knowledge was increased after completion of the program and additional information was received from participants’ feedback substantiating the need for education on advance care planning and related topics.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The use of a web-based learning module is likely to be effective to enhance the knowledge of nurses practicing in a variety of roles and suggests that this method of learning can be implemented in a variety of clinical and community settings. The module content can be tailored to meet the needs of a variety of healthcare and allied health disciplines such as medicine, therapy, and social work to reach many professionals. Concise, state-specific clinical practice guidelines regarding ACP, and the development of a state-wide advance directive repository remain important future recommendations.
POSTER
Dockery, H.D. (2016, October). The Development, Implementation, and Evaluation of a Web-Based Learning Module on Advance Care Planning: Enhancing the Knowledge of Clinical and Advance Practice Nurses in Tennessee. Poster session presented at the Tennessee Nurses Association/Tennessee Association of Student Nurses Annual Joint Convention, Murfreesboro, TN.
-
Dr. Osahon Kings Enodunmwenben
Dr. Osahon Kings Enodunmwenben
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Decreasing Inpatient Readmissions in Homeless Patients
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to identify the problem of inpatient hospital readmission at Hennepin County Medical Center (HCMC) Minneapolis, MN, causes of avoidable readmission and create a Quality Improvement (QI) program for key health officials including essential steps in discharge planning, transitional care, follow-up appointments, and long term care.
METHODOLOGY
A quality management tool (Fishbone diagram) was used to identify, explore and display possible causes of inpatient readmissions. A Retrospective Chart Review (RCR) was conducted using Electronic Medical Records (EMR) at HCMC identifying the patients who were readmitted within 30 – 90 days after discharge from January 1st to December 31st 2015. Convenience sampling was used to compare the readmission rates of housed and homeless patients.
RESULTS
There were 20,962 discharges at HCMC between January 1st and December 31st 2015. There were 4262 who had a risk score of 3. The patients with a priority risk score of 3, had a 1063 (25%) rate of readmissions in 2015 and of these admissions 965 were housed and 98 where homeless. Of the housed patients 25% where readmitted within 30 days, while the homeless group had a 29% readmission rate. Overall, the results from the RCR showed that there is no significant correlation between homelessness and inpatient readmissions at HCMC. Although the rate of readmission was four percentage points higher in homeless patients compared to housed patients, the findings was not statistically significant (p = 0.107).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Based on the results, it is important to specifically address the group with extreme risk score (3) who are frequent users of the Emergency Department (EDs). These patients will be the target of our proposed recommendations. In line with the recommendations from the Institute of Medicine (IOM, 2001), to provide patient care that is “safe, effective, patient-centered, timely, efficient, and equitable”, a quality improvement program was developed that will be disseminated to stakeholders involved in transitional care at HCMC.
-
Dr. Mary Hoft
Dr. Mary Hoft
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Educating First Responders to Identify, Provide Care, and Protect Victims of Human Trafficking
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to increase community first responders’ knowledge and awareness of human trafficking, and improve the ability to identify and respond to the needs of human trafficking victims.
METHODOLOGY
The study was a mixed, quasi-experimental design with a pre-test and 90-minute educational intervention, and included instruction in the use of a screening guide. Three months later post-tests were administered and participant group interviews were conducted.
RESULTS
Quantitative Results: The pre-test mean scores ranged from .5265 to .8395. Post-test mean scores ranged from .6494 to .8395. The within agency means increased between pre- and post-test scores, and increases ranged from .0398 to .1965. The mean score between pre- and post-test scores significantly improved (p < .05) for all but one agency. The pre- and post-test means for the total participants was .5798 and .71968 with a .13928 difference. The paired t-test for total scores was significant at p < .05; total effect size was large (Cohen’s d = 1.084961). Qualitative Results: Themes that emerged from the informal group interviews after post-test completion included: confidence in the ability to recognize trafficking victims, ability to effectively respond to victims, a desire to educate co-workers about human trafficking, a plan to keep the screening protocol available for use in the work setting, change in services to screen for and educate high risk clients about human trafficking, and a desire to collaborate with other participating agencies to develop a coordinated county-wide response to human trafficking
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
This project provided an opportunity for a member of the nursing profession to begin emerging as an expert in human trafficking prevention and highlight the leadership roles advance practice/DNP prepared nurses can assume in this human tragedy that severely impacts the physical and mental health of victims.
-
Dr. Adam Jason Horn
Dr. Adam Jason Horn
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Impacting Inpatient Psychiatric Readmission Rates by Focusing on Subset of High Risk Populations: Determining Characteristics of Subset of High Risk Populations and Releasing Recommendations for Practice
PURPOSE
Readmission rates are being increasingly used as a quality indicator, including possible loss of funding. Psychiatric readmission rates far exceed rates for medical, surgical or maternal/neonatal health readmissions and the local inpatient psychiatric facility in Johnson City, Tennessee exceed the national average. While treatment options are available and effective in reducing readmissions rates for general consumers of inpatient psychiatric treatment, a subset of individuals resistant to traditional interventions exists. This project identifies the characteristics of this subset and develops a protocol for aforementioned facility.
METHODOLOGY
Chart review of the electronic health records of 50 most frequently readmitted to the local inpatient psychiatric facility in Johnson City, TN. Key participants (e.g. discharge planners, prescribers, nursing, administration, etc.) were interviewed for baseline perception of issue. Systems-based, evidence-based treatment recommendations/protocol was developed. Key participants were again interviewed for perception of protocol usefulness.
RESULTS
Protocol developed included increase use of long-acting agents when not contraindicated, admissions to consistent treatment team, brief length of stay defined as two or three day maximum, and referrals to Intensive Outpatient Programs (IOP) available at facility. Key players were overwhelmingly receptive to protocol and conversations regarding implementations
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The results of this study indicate there is a great need and desire for evidence-based guidelines for the reduction of inpatient psychiatric readmission rates among the subset of high utilizers within the psychiatric community. While a significant amount of research has been conducted regarding reduction the reduction of psychiatric readmission rates, little to none has been completed evaluating the subset of high utilizers.
-
Dr. Khairunnissa Aziz Jooma
Dr. Khairunnissa Aziz Jooma
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
PMHNP
TITLE
Educating the Mental Health Providers to become Cultural Competent to identify and provide care regarding Depression in Muslims
PURPOSE
The purpose of this project was to increase the cultural competency skills of mental health providers and assist them in becoming well equipped in assessing, diagnosing and treating depression in Muslims.
METHODOLOGY
A descriptive study applying two theorists, Dr. Madeleine Leininger’s Culture Care and Diversity and Universality theory, and Dr. Campinha-Bacote Cultural Competent Care Model in a pilot format. A convenience sampling method was used to recruit 25 healthcare professionals as participants. Two tools using pre and post implementation survey was conducted and the data analyzed and presented using descriptive statistics.
RESULTS
For both the assessment tools, there was an increase in the range of 68%-73% from pre assessment to post assessment in the levels of cultural competency and knowledge of beliefs and practices regarding treatment in Muslims with depression. For the IAPCC-R the mean pre-test scores was 69.57 (SD = 8.005) and the post-test score was 74.26 (SD = 8.092), The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test revealed that post-test ranks were statistically significantly higher than pre-test ranks (Z = -2.924; p <.003). Within the constructs of the IAPCC-R, the Wilcoxon Signed rank Test revealed increased scores: Cultural awareness: (Z= -3.200; p < 0.001) Cultural Knowledge (Z=-1.997; p <0.046) and Cultural skill (Z= -2.953, p <0.003). For the MCMHS scale, the mean pre-test scores was 61.32 (SD = 8.132) and the post-test score was 66.32 (SD = 8.839). The Wilcoxon Signed-Rank Test revealed that post-test ranks were statistically significantly higher than pre-test ranks (Z = -2.653; p < .008).
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
The findings of this study supports this proponent and highlights the need to educate all mental health providers to become culturally competent in caring of culturally / ethnically diverse population, more specifically focusing on family and community perceptions of mental health and beliefs in treatment when caring for mental illness in Muslims.
Conwill, W.L. & Jooma, K. (2008). Thwarting ethnoviolence against Muslim women: Performing identity in social action. Journal for Social Action in Counseling and Psychology, 1(2), 30-47
-
Dr. Carissa Nichole Myers
Dr. Carissa Nichole Myers
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
AGNP
TITLE
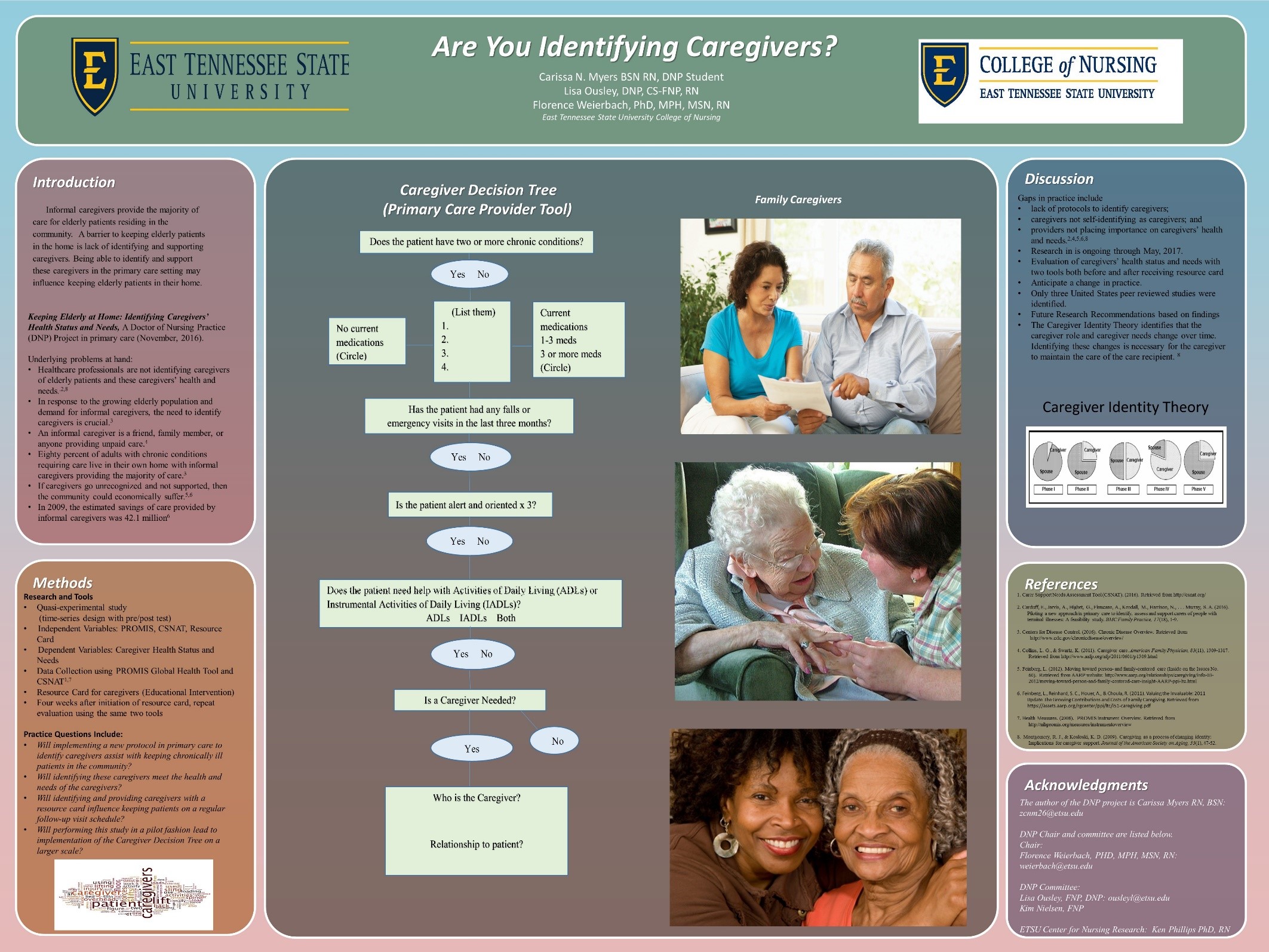
Keeping Elderly at Home: Identifying Caregivers’ Health Status and Needs
PURPOSE
Informal caregivers provide the majority of care for elderly patients residing in the community, but these caregivers are not being accurately identified and supported. Identifying caregivers and supporting caregivers may prevent caregiver burden and loss of identity, with a primary goal of keeping the care recipient in the home longer.
METHODOLOGY
A protocol was developed and implemented to identify informal caregivers using a decision tree in a primary care practice. The caregivers’ perceived health status and needs were then addressed using two tools, and the caregivers were provided with a developed caregiving resource card. Follow-up was conducted in four weeks for reevaluation.
RESULTS
A total of 127 elderly patients were screened using the decision tree, 88 did not need a caregiver, 25 needed a caregiver and had a caregiver, and 14 needed a caregiver but did not have a caregiver. Six caregivers consented to being in the study, and five caregivers completed the screening with the intervention and follow-up. All five of the caregivers reported the resource card being useful and providing awareness to unknown resources.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
A new protocol was implemented to assist with identifying and supporting informal caregivers in a primary care setting. Project analysis showed the importance of screening for informal caregivers among this patient population and providing support to these caregivers to ensure the care recipient stays in the home longer. This protocol pilot may be replicated on a larger scale to further evaluate the Caregiver Decision Tree to identify informal caregivers.
POSTER
Myers, C., Ousley, L, Weierbach, F. (2016, October). Keeping Elderly at Home: Identifying Caregivers’ Health Status and Needs. Poster session presented at the Annual TNA-TASN Joint Conference, Murfreesboro, TN
-
Dr. Denise Ruth Spisso
Dr. Denise Ruth Spisso
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
FNP
TITLE
Medication Reconciliation Implementation in a Rural Health Clinic
PURPOSE
The purpose of the Doctor of Nursing Practice quality improvement project was to implement and evaluate a systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process in a primary care practice in a rural health clinic in Northeast Tennessee.
METHODOLOGY
Implementation of a systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process in a Northeast Tennessee rural health clinic was the primary aim of the project. The objectives of the project focused on implementation of a defined systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process that was inclusive of all patient contact points within the pilot clinic. The objectives were established to comply with federal reporting and aims, identification of data for medication reconciliation analysis and reporting, and determining project impact on patient total clinic visit times. The project identified medication reconciliation data required for analysis of the clinic and individual provider performance. Clinic performance was based on total provider encounters compared with total provider completed medication reviews and medication reconciliations.
RESULTS
A comparison of 3574 patient encounters with completed medication reconciliations Pre- and post-implementation (79.11% and 87.71%) showed a significant increase of 8.6% (p=0.0001). A time impact analysis revealed that implementation occurred with no significant increase in patient total clinic visit times. The findings led to a quality improvement project that was designed to improve medication reconciliation by improving quality, safety, and efficiency of clinical medication management.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Results of the quality improvement project may be used as a guide when implementing a medication reconciliation process within a rural health primary care clinic. Implementing a systematic collaborative medication reconciliation process inclusive of all patient contact points within a clinic supports a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare.
-
Dr. Ramona Craft Whichello
Dr. Ramona Craft Whichello
Degree:DNP
Degree Concentration:
EL
TITLE
Emotional Intelligence in Nurse Administrators
PURPOSE
Health care organizations face tremendous change and complexity. Nurse administrators must develop skills to build and sustain work environments that promote teamwork and positive patient outcomes. Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to perceive emotions, to access and generate emotions, to understand emotions and emotional knowledge, and to regulate emotions. The study examined pre- and post-EI scores for statistically significant improvement after an EI educational offering and evaluated the relationship amongst RN turnover, RN satisfaction, and Total EI scores.
METHODOLOGY
Nurse Administrators at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center (VAMC) were the population of interest and included individuals with job titles of chief nurse operations and acute care, chief nurse geriatrics and extended care, nurse manager, and assistant nurse manager. A one-group pretest-posttest design purposive sample of nurse administrators (n = 13), using the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) to measure EI before and after an EI leadership development offering.
RESULTS
A branch score for managing emotions was significant (p < 0.05). Pre- and post- total EI, area, branch, and task scores were not significant (p > 0.05). Total pre-EI scores showed a low average level of EI (99.89, 98.86 respectively). RN satisfaction was high and RN turnover was low.
IMPLICATION FOR PRACTICE
Leadership development opportunities on emotional intelligence (EI) for nurse administrators are important aspect of continued growth. EI can change over time and may have a positive impact on RN satisfaction ad RN turnover.
Whichello, R.C. (2017, April). Emotional Intelligence: Impact on Teamwork. Team Building Retreat for Learning Resource Center Staff, Asheville, NC
-
2017 DNP Graduates
First Column Second Column Erin Elizabeth Bailey
Jamie Boone
Shaquita Lashea Bonds
Mandy Marie Brannen
Leonard Anthony Dinardo
Holly Dillon Dockery
Charles David Edwards
Osahon Kings Enodunmwenben
Theresa Ann Gibbs
Alan Michael Hicks
Nathan R. Hitchcock
Mary Hoft
James Marett HolbrookAdam Jason Horn
Khairunnissa Jooma Aziz
Leslie Moro
Carissa Nichole Myers
Paige Noel Reed
Deana McThenia Rhinehart
Holly Kaimanakea Gyure Sawyer
Ashley Nicole Shouse
Denise Ruth Spisso
Krissa Marie Trombetta
Ramona Craft Whichello
Dorie Wykes
2024.12.05.01 v. 41 | Associate Dean for Graduate Programs
 Stout Drive Road Closure
Stout Drive Road Closure